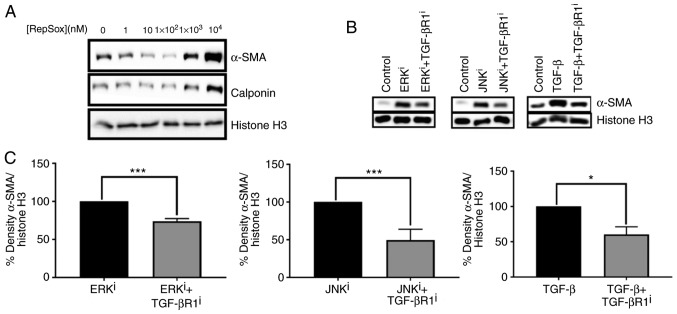
Figure 6.
Effects of TGF-βR1 inhibition on fibroblast activation induced by ERK or JNK inhibitors. (A) CRL-2097 human dermal fibroblasts were cultured in the presence or absence of the indicated concentration of the TGF-βR1 inhibitor RepSox until day 4 and then subjected to Western blot analysis for myofibroblast markers α-SMA and calponin. Histone H3 was used as a loading control. (B) CRL-2097 human dermal fibroblasts were cultured in the presence or absence of 10 µM U0126 (ERKi), 10 µM SP600125 (JNKi), 10 ng/ml TGF-β1 and 100 nM RepSox until day 4 and then subjected to western blot analysis for myofibroblast marker α-SMA. Histone H3 was used as a loading control. (C) Western blots were analyzed using densitometry, and relative density of α-SMA/Histone H3 was compared for each mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor-treated or TGF-β1-treated sample compared with its corresponding TGF-βR1 inhibitor-treated sample. Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001. There were 2≤n≤4 biological replicates/condition. Error bars depict the standard deviation. TGF-βR1, transforming growth factor-β receptor 1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; α-SMA, smooth muscle α actin; i, inhibitor.