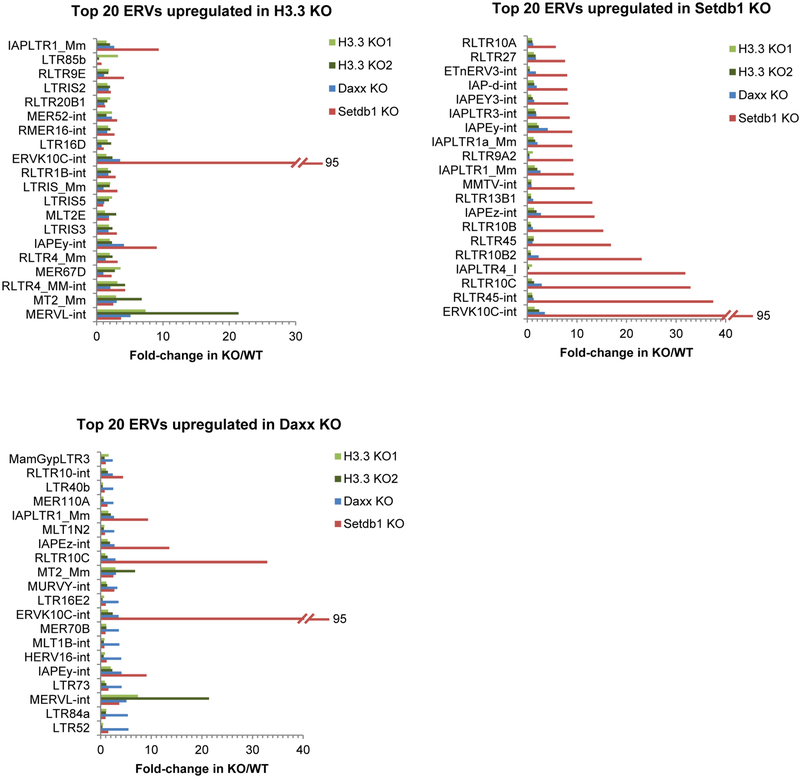
Extended Data Figure 3 |. ERV expression in Setdb1-, H3.3- and Daxx-knockout ES cells.
The fold change in expression over the corresponding wild-type control is shown for the top 20 upregulated ERV annotations in Setdb1-, H3.3- and Daxx-knockout ES cells. Annotations including –int represent the internal regions, which are transcribed from the cognate 5′ LTR, of the annotated ERV. For example, ERVK10C-int is the internal region of ERVK10C elements, with flanking LTRs: RLTR10A, RLTR10B and RLTR10C (depending on the specific genomic copy), which are also presented among the graphs. Similarly, IAPEz-int is the internal region of IAPEz elements with flanking cognate LTRs: IAPLTR1_Mm and IAPLTR1a_Mm, which are also represented. As the internal region is much longer and transcribed across its length, this is the most useful annotation to consider for expression analysis. The following published RNA-seq GEO data were re-analysed: GSM727424 (Setdb1-knockout ES cells); GSM1428580 and GSM1428581 (H3.3-knockout ES cells). Only ERV groups with more than 100 family members were considered for analysis.