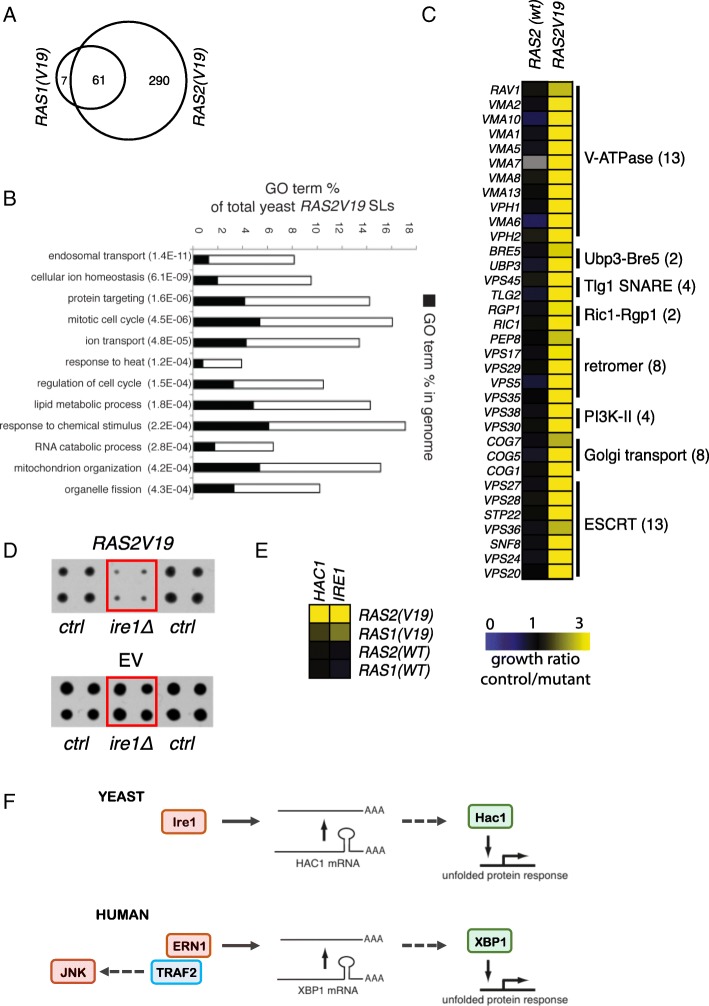
Fig. 1.
Unfolded protein response (UPR) executors are synthetic lethal with mutant RAS in S. cerevisiae. a Venn diagram showing the overlap of the RAS synthetic lethal (SL) gene deletion strains identified in the RAS1(V19) and RAS2(V19) genetic screens. b Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis on the SL gene deletion strains from the RAS2(V19) screen identifies a variety of biological processes, including endosomal transport and protein targeting. c List of genes coding for protein complexes among the validated list of RAS2(V19) SL gene deletion mutants. Higher values correspond to stronger growth arrest in the presence of mutant RAS. The pathways and complexes in which the genes are involved are indicated. d The effect of the deletion of the UPR stress sensor IRE1 (ire1Δ) in RAS2(V19) screen (top) and in the empty vector (EV) control background (bottom). e Control vs mutant growth ratios of the UPR genes IRE1 and HAC1. Higher values correspond to stronger growth arrest in the presence of mutant RAS. f Schematic representation of the evolutionary conserved mechanism of UPR execution in yeast (top) and humans (bottom). Ire1 is responsible for the editing of HAC1 mRNA which produces an active executor of the UPR. ERN1 is the human ortholog of yeast IRE1; XBP1 is a functional human homolog of HAC1