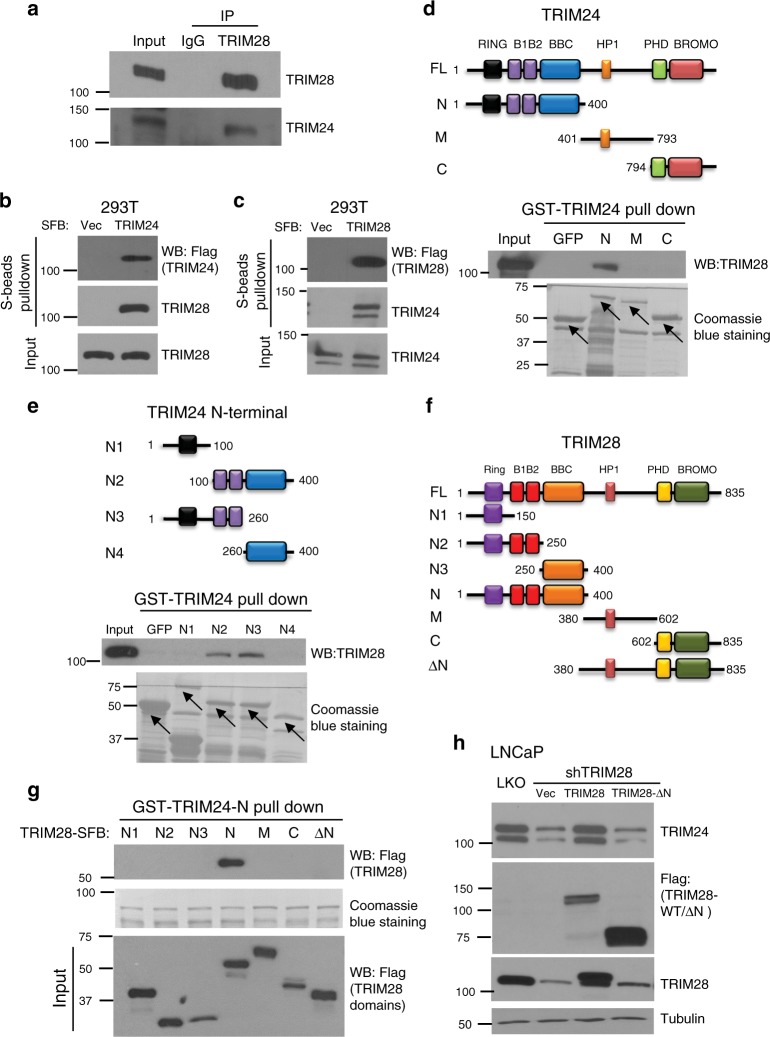
Fig. 2.
Physical interaction with TRIM28 is required for TRIM24 protein stability. a TRIM24 interacts with TRIM28 in vivo. LNCaP cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using a TRIM28 antibody and the eluted protein was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-TRIM24 and anti-TRIM28 antibodies. b, c TRIM28 and TRIM24 proteins interact. 293T protein lysates expressing TRIM24-SFB (b) or TRIM28-SFB (c) was pulled down by S-beads and eluted proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. d, e TRIM24 utilizes N-terminal B1B2 domain to interact with TRIM28. Schematic illustration of a series of TRIM24 deletion mutants used in this study (upper panel, d, e). Bacterially expressed and purified GST-tagged TRIM24 mutants or GFP (negative control) coupled to GSH beads were used to pull-down LNCaP protein lysates. The precipitated protein complexes were subjected to western blot analysis using anti-TRIM28 antibody (lower panel, d, e). Coomassie blue was used to stain GST-tagged protein coupled to the beads. Arrow depicts intact protein. f, g. N-terminal region of TRIM28 interacts with TRIM24. Schematic illustration of wild-type and deletion mutants of TRIM28 used in this study (f). Bacterial recombinant GST-TRIM24 (1–400aa) protein was incubated with LNCaP cell lysates expressing various SFB-tagged TRIM28 deletion mutants. GST (TRIM2 1–400aa) pull-down were performed using GSH beads and eluted proteins were analyzed with use of anti-flag antibody to detect SFB-tagged TRIM28 deletion mutants (g). h Physical interaction with TRIm28 is required for TRIM24 stabilization. LNCaP cells expressing pLKO, shTRIM28, co-expressing shTRIM28 + TRIM28 wild-type or shTRIM28 + TRIM28-ΔN-SFB (TRIM24 binding-deficient mutant) were harvested and protein lysates was subjected to immunoblotting using indicated antibodies