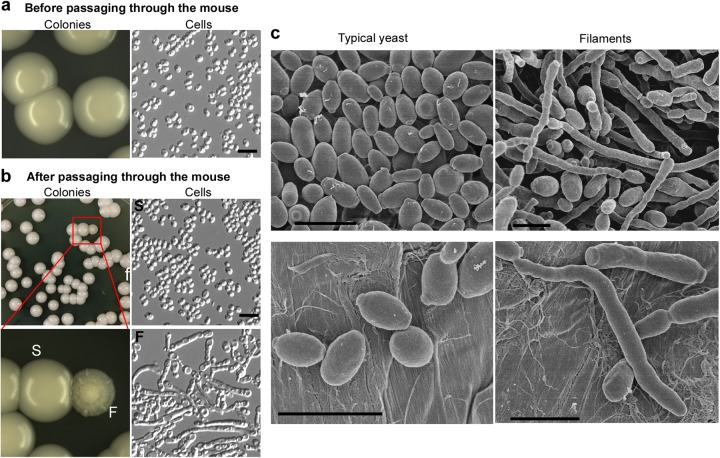
Fig. 1. Observed colony and cellular morphologies of C. auris.
a No filamentous colonies observed before passaging the animal. C. auris cells were grown on YPD medium for 2 days at 30 °C and then switched to 25 °C for five additional days. No filamentous colonies were observed (switching frequency < 0.001%). b Passage through the animal induces the filamentous morphology. C. auris cells were injected into mouse tail veins; cells were recovered from liver, kidney, brain, lung, and spleen tissues 24 h postinfection and replated on YPD medium. After 2 days of incubation at 30 °C, the cultures were then transferred to 25 °C for five additional days of incubation. Colonies shown were recovered from the liver and characterized as: smooth/typical yeast (S) or filamentous (F). Switching frequencies of typical yeast to filamentous colonies were (0.1 ± 0.2)% in the liver (colonies shown in the figure) and (0.4 ± 0.2)% in the kidney, respectively (totally, about 4000 colonies were analyzed). Scale bar represents 10 μm. c Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of typical yeast and filamentous C. auris cells. C. auris cells were grown on YPD medium at 37 °C for 3 days and then switched at 25°C for three additional days of incubation. Scale bar represents 5 μm