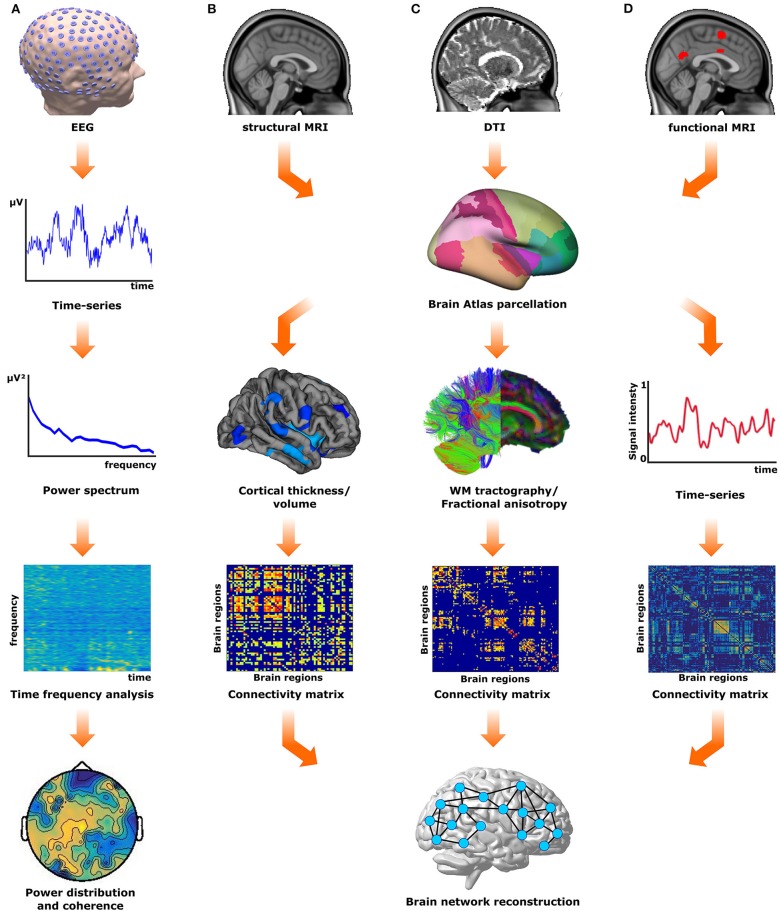
Figure 1.
Overview of network reconstruction methods. (A) The electrical activity of the brain is recorded using electroencephalography (EEG). These recordings (EEG time-series) are analyzed using time-frequency analysis approaches to investigate the spatiotemporal distribution of the frequency power. (B) From structural (T1) magnetic resonance images (MRI) morphological measures (cortical thickness/volume) for different brain regions can be extracted according to a predefined atlas. These measures are used to obtain a structural covariance matrix, from which the structural gray matter network is reconstructed. (C) The diffusion tensor images (DTI) are used to derive white matter tracts, from either probabilistic or deterministic tractography algorithms, or fractional anisotropy maps. These measures are used to obtain a connectivity matrix according to the brain atlas of choice, and subsequently, the structural white matter network is reconstructed. (D) The functional MRI (fMRI) time series from different brain regions obtained can also be used to generate the functional connectivity matrix and subsequently to reconstruct the functional brain network.