Fig. 1.
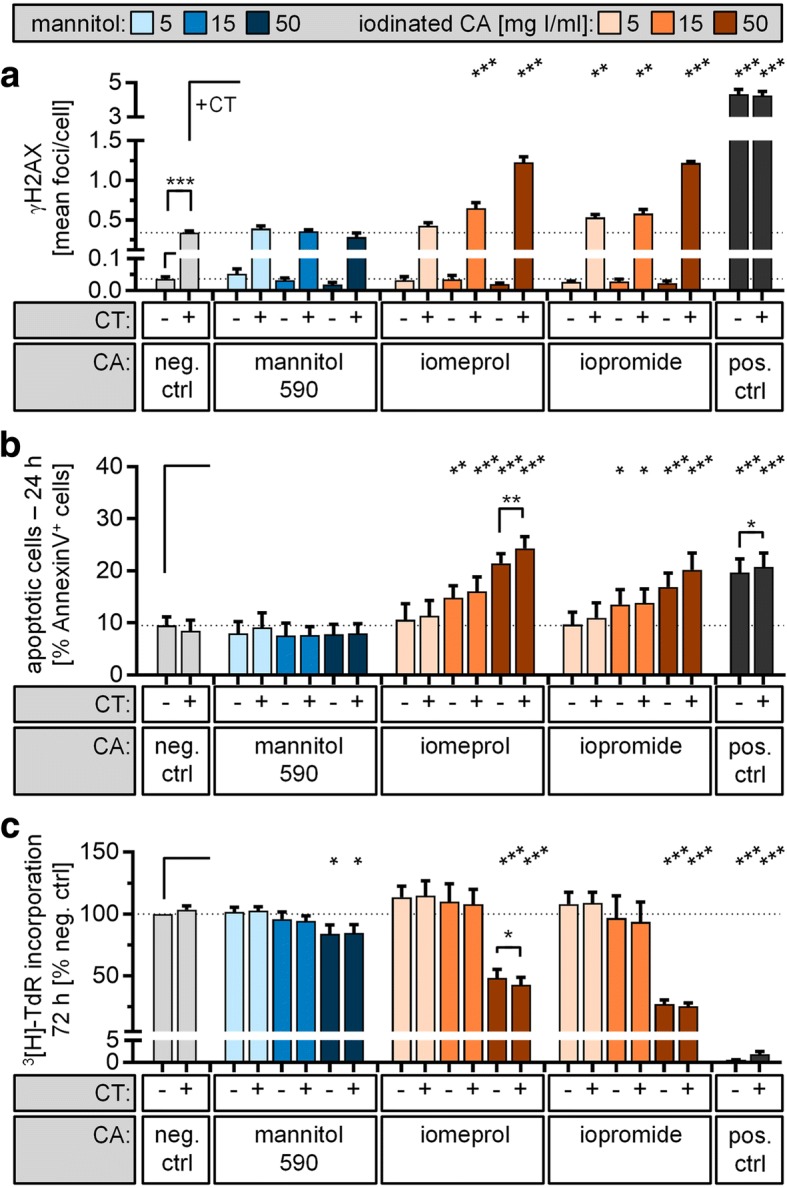
Genotoxic and cytotoxic impact of contrast-enhanced CT exposure. Isolated lymphocytes were incubated with indicated concentrations of iomeprol or iopromid. Samples incubated in cell culture medium only (neg. ctrl) or with mannitol solution with the same osmolality as iopromide (590 mOsm/kg H2O) served as negative controls. Additionally, samples were either irradiated by a thorax CT scan (+) or placed outside the CT scanner (-) at the same temperature. a The level of DNA double-strand breaks was assessed 15 min after CT exposure by γH2AX staining and automated foci quantification. Lymphocytes irradiated with 0.5 Gy served as positive controls (pos. ctrl). b Apoptosis rate was quantified after 24 h by Annexin V/propidium iodide staining combined with flow cytometric analysis. Samples incubated with 2 μM camptothecin served as positive controls. c For proliferation analysis, lymphocytes were activated with PHA directly after CT exposure. Level of DNA synthesis was determined after 72 h by [3H]-thymidine incorporation. Lymphocytes treated with 2 μM camptothecin served as positive controls. Diagrams displays mean ± standard error of the mean of four experiments (***p ≤ 0.001; **p ≤ 0.01; *p ≤ 0.05) and raw data are listed in Additional file 1: Tables S1–S3
