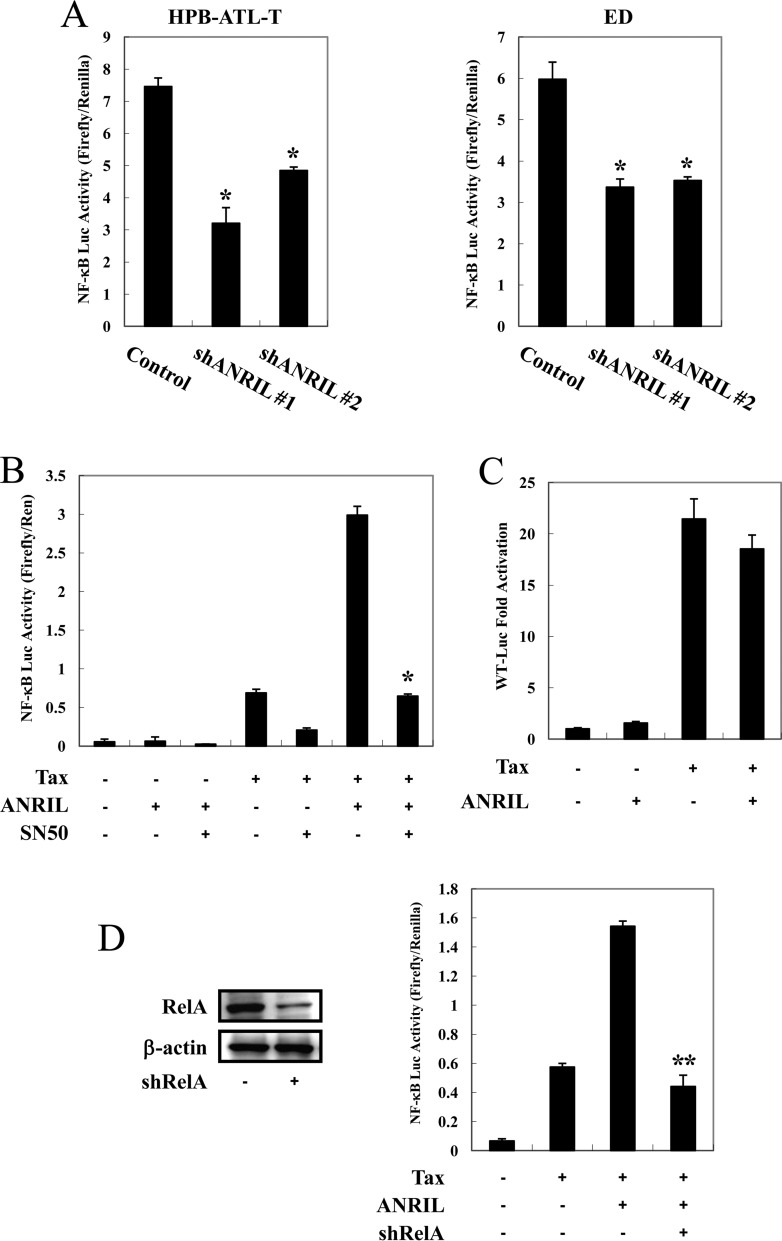
FIG 5.
ANRIL/Tax-mediated NF-κB activation is dependent on p65. (A) Inhibition of NF-κB signaling by ANRIL knockdown. ANRIL knockdown HPB-ATL-T (left) and ED (right) cells were cotransfected with κB-Luc and phRL-TK plasmids. Luciferase levels were measured after 48 h. (B) SN50 suppresses Tax- and ANRIL-induced NF-κB activation. Jurkat cells were cotransfected with κB-Luc (0.5 μg), phRL-TK (20 ng), pCG-Tax (0.5 μg), and pCSII-CMV-ANRIL (0.5 μg). Twenty-four hours after transfection, SN50 (20 μM) was added. After 24 h, the cells were harvested and analyzed for luciferase activity. (C) ANRIL does not influence Tax-mediated transcriptional activation from the HTLV-1 promoter. Jurkat cells were cotransfected with WT-Luc, phRL-TK, pCG-Tax, and pCSII-CMV-ANRIL. After 48 h, the cells were harvested and analyzed for luciferase activity. (D) Silencing of RelA/p65 expression impairs ANRIL- and Tax-mediated NF-κB activation. HPB-ATL-T cells were transfected with a recombinant lentivirus expressing pLKO-shRelA/p65. p65 knockdown cells were cotransfected with κB-Luc and phRL-TK plasmids. After 48 h, the expression levels of p65 and β-actin were analyzed by immunoblotting (left), and the cells were harvested and analyzed for luciferase activity (right). All the data shown are relative values of firefly luciferase normalized to the value for Renilla luciferase and expressed as means of results from a triplicate set of experiments (±SD). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.