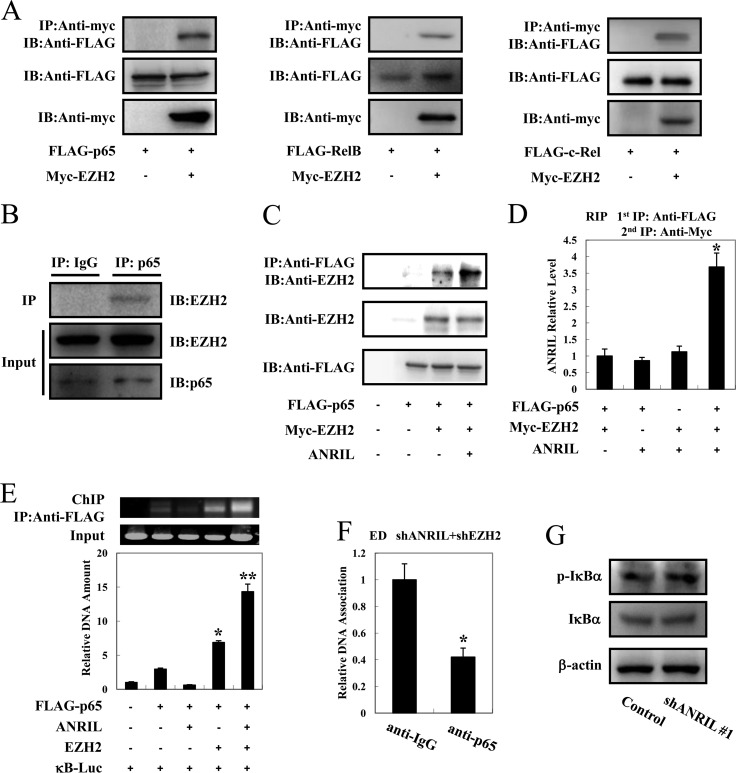
FIG 7.
ANRIL forms a complex with EZH2/p65 and enhances the NF-κB pathway. (A) EZH2 interacts with p65, RelB, and c-Rel. 293FT cells were cotransfected with lenti-Myc-EZH2 together with FLAG-p65 (left), FLAG-RelB (middle), or FLAG–c-Rel (right). After 48 h, cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-c-Myc followed by immunoblotting (IB) using anti-FLAG. (B) The interaction between endogenous EZH2 and p65 in HPB-ATL-T cells was analyzed by an immunoprecipitation assay. (C) ANRIL enhances the interaction between EZH2 and p65. 293FT cells were cotransfected with lenti-Myc-EZH2, pCSII-CMV-ANRIL, and pCMV-p65. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG followed by immunoblotting with anti-EZH2. (D) ANRIL, EZH2, and p65 can form a ternary complex. pCSII-CMV-ANRIL, lenti-Myc-EZH2, and pCMV-p65 were cotransfected into 293FT cells. Ternary complexes were detected by sequential immunoprecipitation with an anti-FLAG agarose affinity gel and anti-Myc antibody, and coprecipitated RNAs were detected by PCR. (E) ANRIL/EZH2 enhances p65 DNA binding capability. After transfection with lenti-Myc-EZH2, pCSII-CMV-ANRIL, pCMV-p65, and κB-Luc for 48 h, 293FT cells were chromatin immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG antibody. The precipitated DNAs and 1% of the input cell lysates were amplified by the κB-Luc-specific primers (top, RT-PCR; bottom, real-time PCR). (F) Silencing of ANRIL and EZH2 inhibits p65 DNA binding capability. ANRIL knockdown cells were transfected with a recombinant lentivirus expressing pLKO-shEZH2. After puromycin selection, the binding of p65 to the NF-κB binding site of the MYC gene was analyzed by a ChIP assay. (G) Silencing of ANRIL does not influence phosphorylation levels of IκBα. After knockdown of ANRIL, the phosphorylation level of IκBα was analyzed by immunoblotting. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.