Figure 2.
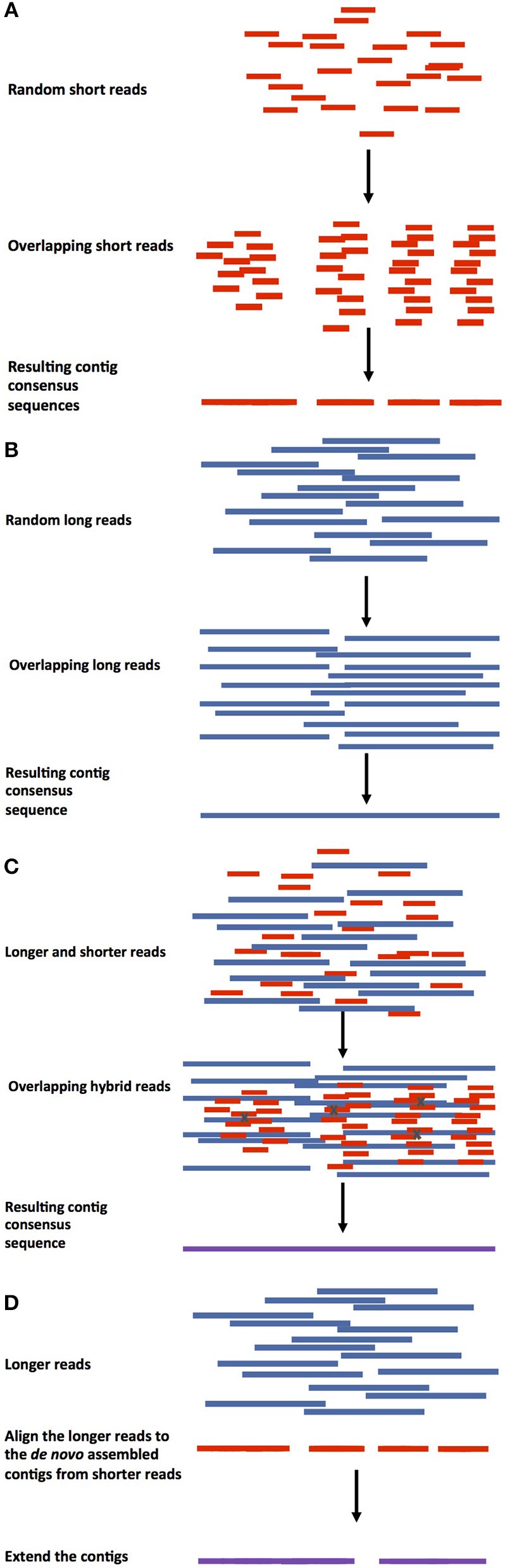
Approaches for de novo assembly genome approaches. (A) Short read assembly. Genome assembly using only shorter reads and any assembly tool to construct contiguous sequences/contigs. (B) Longer reads assembly. Contig (red) assembly using longer reads (long, linked reads, optical maps) followed by scaffold assembly and gap filling. (C) Hybrid genome assembly. In this method, shorter reads can be assembled into contigs and the longer reads can be used for error correction (errors represented by Xs), then the corrected contigs can be assembled into scaffolds and the gaps filled. (D) Hybrid genome assembly using pre-assembled contigs. Longer reads are aligned against de novo pre-assembled contigs from shorter reads, followed by contig extension.
