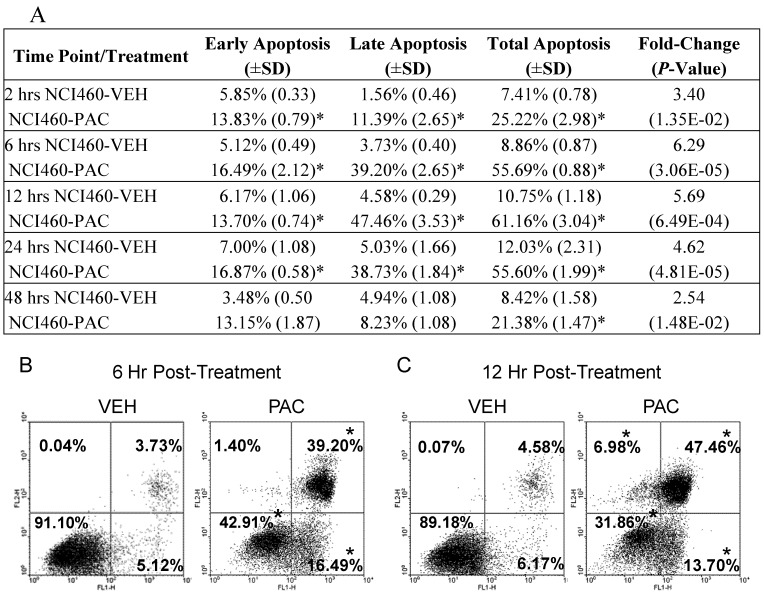
Figure 2.
PAC (50 μg/mL) induces cell death in NCI-H460 lung cancer cells. (A) summary of the effects of PAC on early, late and total apoptosis at 2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 hours post-treatment as determined by Annexin V-FITC staining. PAC treatment induced significant early apoptosis (B and C, lower right quadrant), late apoptosis (upper right quadrant) and total apoptosis at 2, 6, 12, and 24 hours. The largest magnitude of apoptosis induction occurred following 6 and 12 hours of treatment as illustrated in (B) and (C). PAC induces significant necrosis (C, upper left quadrant) following 12 and 24 hours of PAC treatment as evidenced by the increase from <1.00% necrosis in vehicle treated NCI-H460 cells to 6.98% in PAC treated cells 12 hours post-exposure. The values represent means ±SD of three independent samples per experimental treatment and time-point (P < 0.05, two-tailed t test). Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference between PAC and vehicle treated cells. Reported fold-change values refer to the fold-change induced by PAC treatment compared to vehicle in terms of total apoptosis induction.