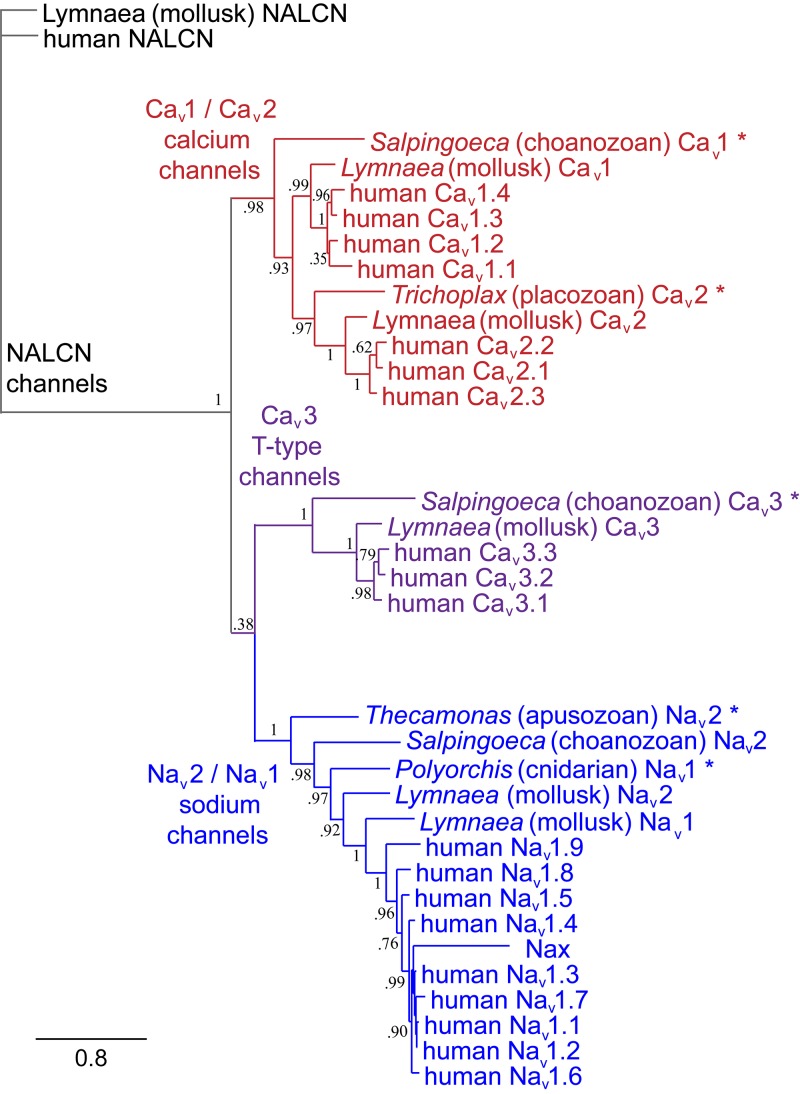
FIGURE 1.
Gene tree of 4 × 6 TM (TM = transmembrane) voltage-gated sodium channel α subunits (Nav1 and Nav2), calcium channel α1 subunits (Cav1, Cav2, and Cav3) and NALCN. Included in the multiple alignment are the 21 human homologs and the 6 homologs from representative protostome invertebrate, pulmonate snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. Basal genes of each class (indicated in bold and ∗) including apusozoan, Thecamonas trahens (Nav2), single cell choanoflagellate, Salpingoeca rosetta (Cav1 and Cav3), placozoan, Trichoplax adhaerens (Cav2), and cnidarians (hydrozoan jellyfish), Polyorchis penicillatus (Nav1). More distant Na Leak Conductance channel (NALCN) serve as the out-group for the phylogenetic tree. Bootstrap values are shown at the nodes. Notably weak branch strength is in the positioning for Cav3 T-type channels which is relatively equidistant from sodium channels and other calcium channels. The gene tree illustrate the close kinship amongst Nav2 and Nav1 channels and between Cav1 and Cav2 channels. Amino acid sequences were aligned using MUSCLE 3.7 (Edgar, 2004) within EMBL-EBI web interface (Chojnacki et al., 2017). Gene trees were constructed in PhyML 3.0 (Guindon et al., 2010) using Phylogeny.fr web interface (Dereeper et al., 2008).