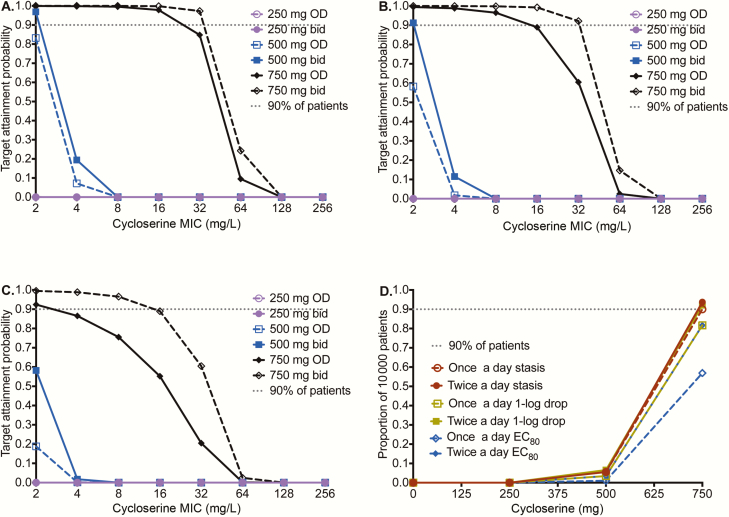
Figure 4.
Performance of different d-cycloserine doses for pulmonary disease. d-cycloserine minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) based on the Sensititre assay were used. A, For the stasis target (ie, exposure at which there is no kill or growth compared to day 0), the target attainment probabilities (TAPs) are shown for doses of 250–750 mg at 2 dosing schedules. There is clear separation of performance by the 750-mg doses (shown in black) from the rest of the doses. At 750 mg daily, TAP falls at MICs of ≥32 mg/L. B, For cidal activity, the same pattern is shown, except that now there is also separation of TAPs between 750 mg once daily and 750 mg twice daily. At the latter dose and schedule, the MIC above which TAP falls below 90% is 32 mg/L. C, For the target of 80% of maximal kill (EC80), even the dose if 750 mg twice a day would fall below 90% at around 32 mg/L. D, When an expectation was taken over the entire MIC range, the dose of 750 mg twice daily was able to achieve the exposure target of stasis, cidal effect, and EC80, in 93%, 92%, and 81% of 10000 patients, respectively. Abbreviations: bid, twice daily; EC80, 80% of maximal kill; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; OD, once daily.