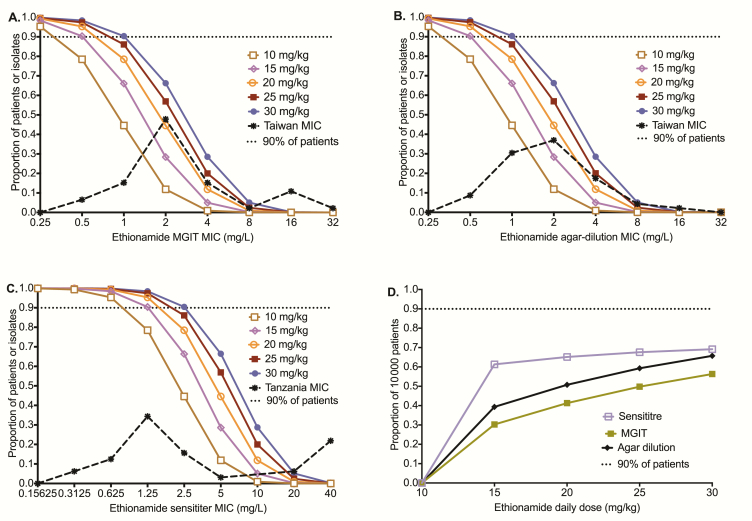
Figure 3.
Monte Carlo simulation results for 10000 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Target attainment probability (TAP) is the proportion of 10000 patients who achieve target exposure at a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The TAP fell as the MIC rose. Since the type of MIC assay affects the MIC distribution, we examined the TAP using 3 MIC assays. (A) For MGIT-based MICs from Taiwan isolates, the TAP for the standard dose of 15–20 mg/kg/day falls below 90% at an MIC of 1.0 mg/L, which should be the clinical breakpoint for this dose. (B) TAP using agar dilution–based MICs, which are the gold standard, was similar to that for MGIT based. (C) When we used the Sensititre assay-based MIC for our laboratory strain to calculate target area under the concentration time curve (AUC)/MIC and the Sensititre-based MIC of clinical isolates, the ethionamide 15–20 mg/kg/day dose achieved a TAP which fell below 90% at the MIC of 2.5 mg/L, which should be the proposed MIC clinical breakpoint at these doses. At a dose of 30 mg/kg/day, the proposed clinical breakpoint MIC is 5 mg/L. (D) The cumulative fraction of response for different doses examined is a summation over all MICs. Abbreviation: MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration.