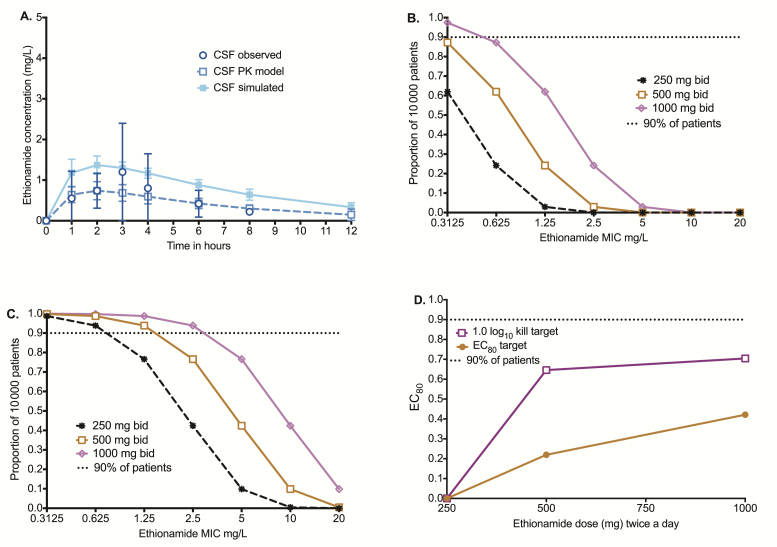
Figure 4.
Target attainment in 10000 patients with tuberculous meningitis. (A) Population pharmacokinetics-based simulation of concentration-time profiles in the cerebral spinal fluid vs that observed in patients shows that simulation-derived concentrations were similar to those seen in patients. (B) The target attainment probability (TAP) of doses of 250–1000 mg twice a day for the exposure associated with 80% of maximal kill (EC80 target) was poor regardless of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). (C) For the target of 1.0 log10 colony-forming units/mL kill (cidal effect), the TAP for 1000 mg twice a day was >90% up to an MIC of 2.5 mg/L. (D) For the 250 mg twice a day dose, the cumulative fraction of response (CFR) was 0% for both the cidal effect and EC80 targets. As regards to the 500-mg twice a day dose, the CFRs were 64% and 21% for the cidal effect and EC80 targets, respectively. The CFRs for the 1.0 log10 kill did not improve much with the 1000-mg BID dose but went up substantially for the EC80 target. Abbreviations: bid, twice daily; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; EC80, exposure associated with 80% of maximal kill; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; PK, pharmacokinetic.