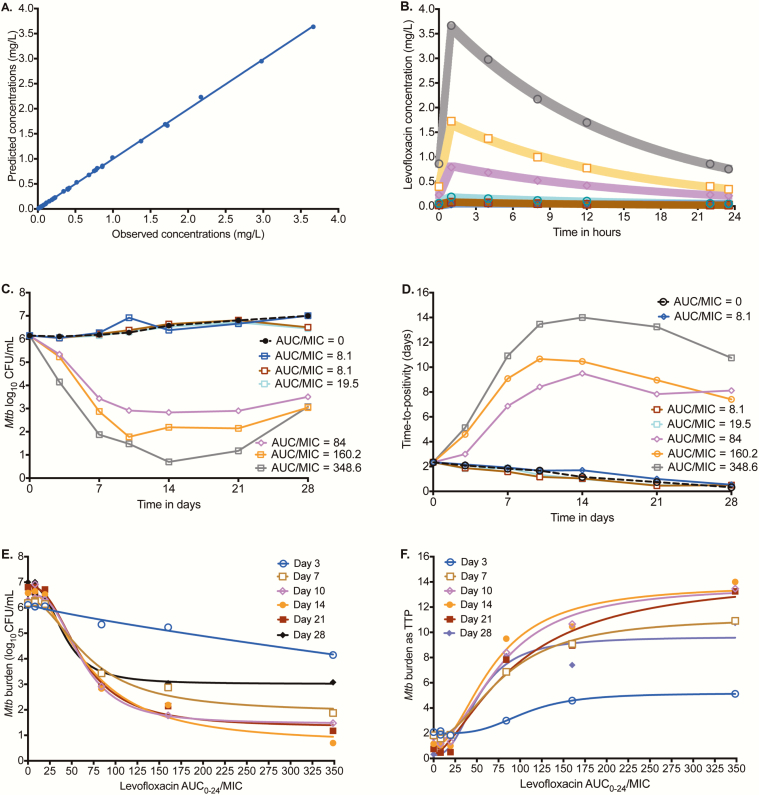
Figure 2.
Levofloxacin pharmacokinetics (PKs) and time-kill curves in the hollow fiber system model of tuberculosis (HFS-TB). (A) Model-predicted vs observed levofloxacin concentrations in the hollow fiber system. (B) Levofloxacin concentrations achieved in each HFS-TB at each time point were used for PK modeling. The shaded area is the 95% confidence interval for the PK model-derived concentrations for each dose; the observed concentrations show that the model described the data well. (C) Time change in colony-forming units per milliliter (CFU/mL) with duration of therapy shows that the exposures could be separated into 2 groups. The highest exposure achieved near sterilization on day 14, followed by rebound on day 21. (D) Time-to-positivity (TTP) shows the same pattern as with CFU/mL. (E) The inhibitory sigmoid maximal kill (Emax) model curves are shown based on the CFU/mL readout. (F) Inhibitory sigmoid Emax modeling using TTP as a measure of bacterial burden demonstrated a higher exposure associated with 50% of maximal kill than was observed for CFU/mL. Abbreviations: AUC0-24, 0–24 hour area under the concentration-time curve; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; Mtb, Mycobacterium tuberculosis.