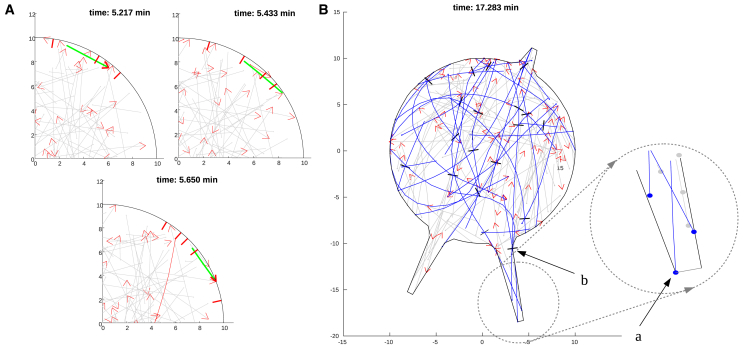
Figure 3.
Simulations of motor-perturbed cells. (A) Simulations of cells after kinesin inhibition are shown. Cortex-bound dynein motors push MTs tangentially along the cortex and therefore do not initiate processes. One MT that is being slid by dynein along the cell boundary in this simulation is shown in green. One MT starts to interact with a dynein motor at the later time and is shown in red. (B) Process elongation driven by kinesins (black bars) in dynein-inhibited cells is shown. Kinesin motors, such as the one shown in (b), push against the process tips through MT minus ends (filled circles at the MT ends in the inset marked in (a)). MTs being pushed by kinesin are shown in blue. In both (A) and (B), MTs not interacting with the motors are shown in gray; growing MT plus ends are indicated by the red arrows. To see this figure in color, go online.