Figure 2.
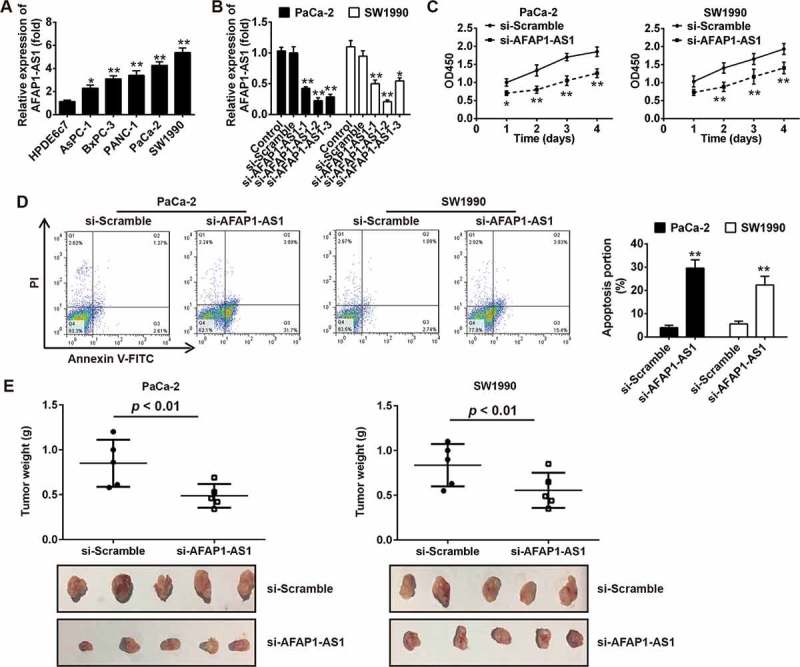
Knockdown of AFAP1-AS1 suppressed tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. (a) RT-PCR analysis of AFAP1-AS1 expression levels in PC cells (AsPC-1, BxPC-3, PANC-1, PaCa-2 and SW1990) and primary cultures of normal human pancreatic duct epithelial cells (HPDE6c7) used as a control. Data are represented as means ± S.D. from three independent experiments, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. HPDE6c7. (b) qRT-PCR analysis of AFAP1-AS1 expression levels in PaCa-2 and SW1990 cells after siRNA transfection. Data are represented as the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. si-Scramble or control. (c) The effect of AFAP1-AS1 knockdown on the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells was determined by CCK-8 assays. Data are represented as the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. si-Scramble. (d) The effect of AFAP1-AS1 knockdown on the cell apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry. Data are represented as the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments, **p < 0.01 vs. si-Scramble. (e) Tumor weight changes in the mice bearing PaCa-2 and SW1990 cells with si-AFAP1-AS1 or si-Scramble. si-AFAP1-AS1 vs. si-Scramble, p < 0.01.
