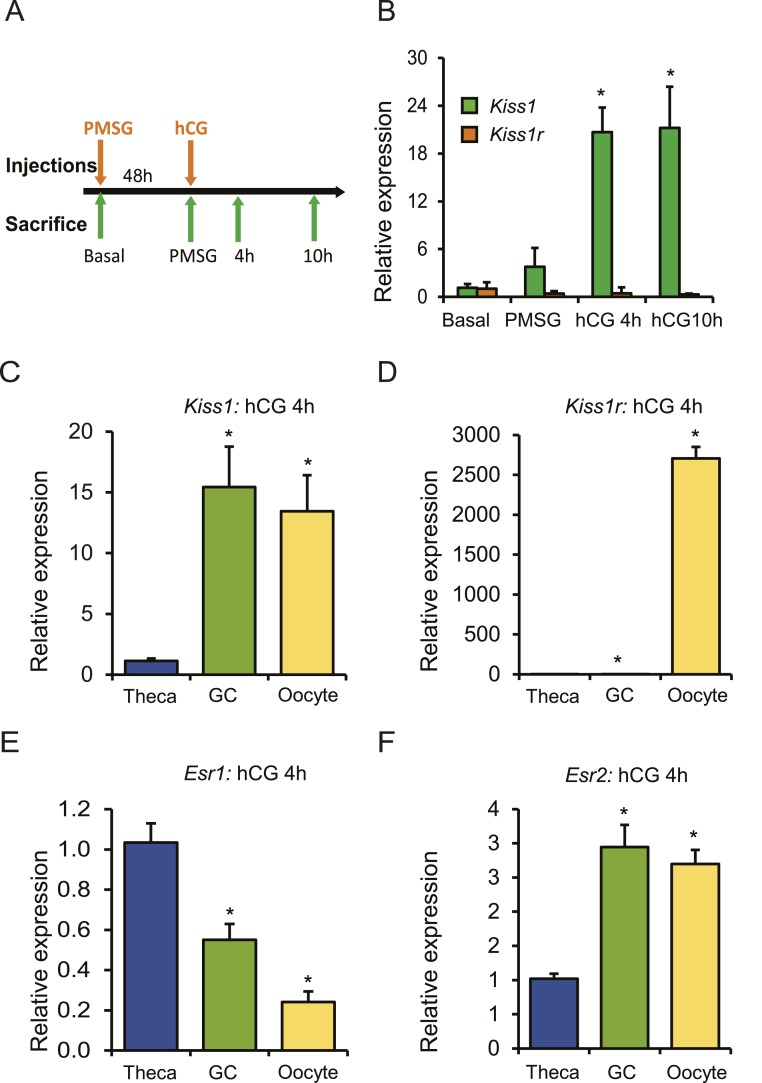
Figure 1.
Expression of Kiss1 is induced by gonadotropin administration. (A) Four-week-old wild-type female rats were treated with gonadotropins, and the ovaries were collected at the indicated time points for RNA isolation and qRT-PCR analyses. (B) Kiss1 expression increased significantly 4 h after hCG injection and remained elevated at 10 h after hCG. However, the expression of Kiss1r did not show any changes after gonadotropin stimulation. (C) Ovaries were collected 4 h after hCG administration for the isolation of oocytes, granulosa cells, and thecal-interstitial tissues. qRT-PCR analyses showed that Kiss1 expression was significantly higher in granulosa cells and oocytes compared with theca cells. (D) But expression of Kiss1r was detected exclusively in the oocytes. (E) Expression of Esr1 was significantly higher in theca cells compared with granulosa cells or oocytes. (F) In contrast, expression of Esr2 was significantly higher in granulosa cells and oocytes coinciding with Kiss1 expression. qRT-PCR data are represented as mean ± SEM. n = 6. *P ≤ 0.05. GC, granulosa cell.