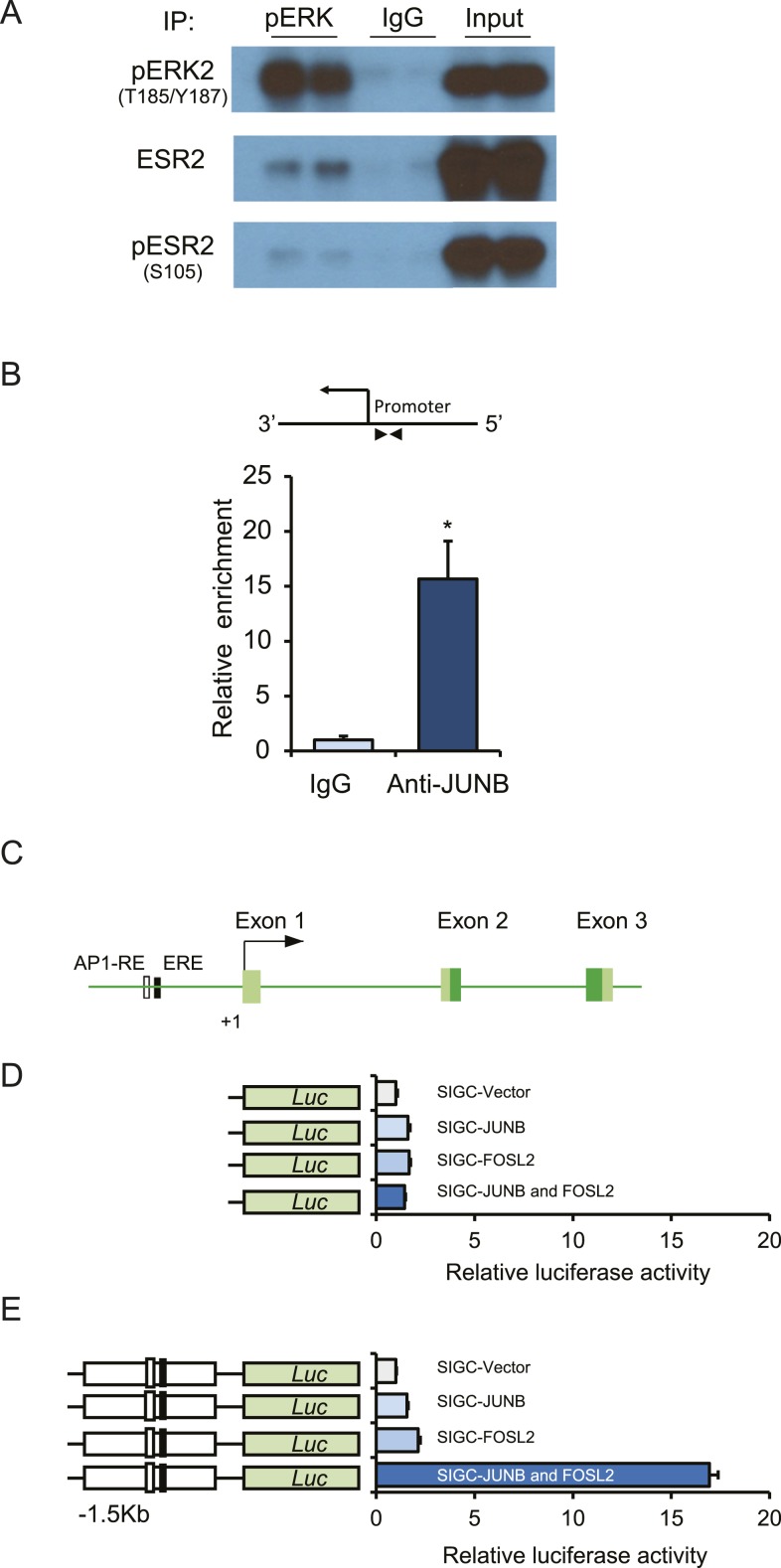
Figure 6.
Activated ERK2 interacts with ESR2, and AP-1 factors can activate Kiss1 promoter. Protein complex formation was determined by a coimmunoprecipitation assay using protein extracts prepared from granulosa cells isolated from PMSG-primed, hCG-treated immature rats. Immunoprecipitation was performed with a rabbit monoclonal antibody to pERK1/2 or normal rabbit IgG. The immunoprecipitates were then subjected to Western blot analyses with pERK1/2, ESR2, and pESR2 antibodies. (A) We observed that pERK2 was coimmunoprecipitated with ESR2. (B) ChIP assays were performed on gonadotropin-stimulated rat granulosa cells with an anti-JUNB rabbit monoclonal antibody. Normal rabbit IgG was used as a negative control. ChIP-qPCR results demonstrated a relative enrichment of JUNB at the Kiss1 promoter. (C) Schematic diagram of Kiss1 promoter indicating presence of a potential ESR2 binding (ERE) and AP-1 binding sites. Luciferase assays were performed after cotransfecting (D) the empty pGL4.12 luciferase vector or (E) pGL4.25 vector carrying 1.5 kb of the Kiss1 promoter along with AP-1 factors JUNB or FOSL2 into SIGC cells. (D, E) Empty pGL4.12 vector exhibited a minimal induction of luciferase activity after either JUNB or FOSL2 overexpression, whereas (E) the relative luciferase activity of the reporter constructs with 1.5 kb of Kiss1 promoter harboring an AP-1 RE site showed a marked upregulation when both JUNB and FOSL2 were cotransfected. Relative luciferase data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments in duplicate wells. n = 6. *P ≤ 0.05. Luc, luciferase.