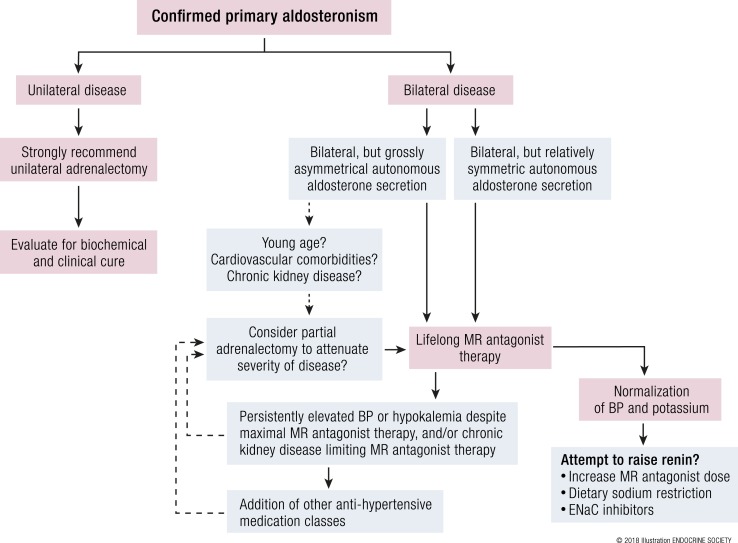
Figure 8.
Modified proposal toward the treatment of primary aldosteronism. The conventional approach to treating primary aldosteronism dictates that surgical adrenalectomy is preferred when there is unilateral disease, and lifelong MR antagonist therapy is preferred for bilateral disease. The pink boxes represent the conventional approach to treatment. The blue boxes represent the authors’ modified proposal toward treatment. Adrenal venous sampling provides results for lateralization, but it can also quantify the degree of relative autonomous aldosterone secretion from each adrenal vein. For patients with known cardiovascular or renal disease and who have grossly asymmetric bilateral primary aldosteronism, unilateral adrenalectomy to attenuate the severity of disease may be considered. When lifelong MR antagonist therapy is employed, the objective is to normalize blood pressure and potassium, and when possible, titrate the dose of the medication to achieve a rise in renin as a biomarker for sufficient MR blockade. When blood pressure or potassium cannot be effectively normalized with MR antagonist therapy, or chronic kidney disease limits the aggressiveness with which these medications can be used, unilateral adrenalectomy and/or additional antihypertensives could be considered. BP, blood pressure. [© 2018 Illustration ENDOCRINE SOCIETY]