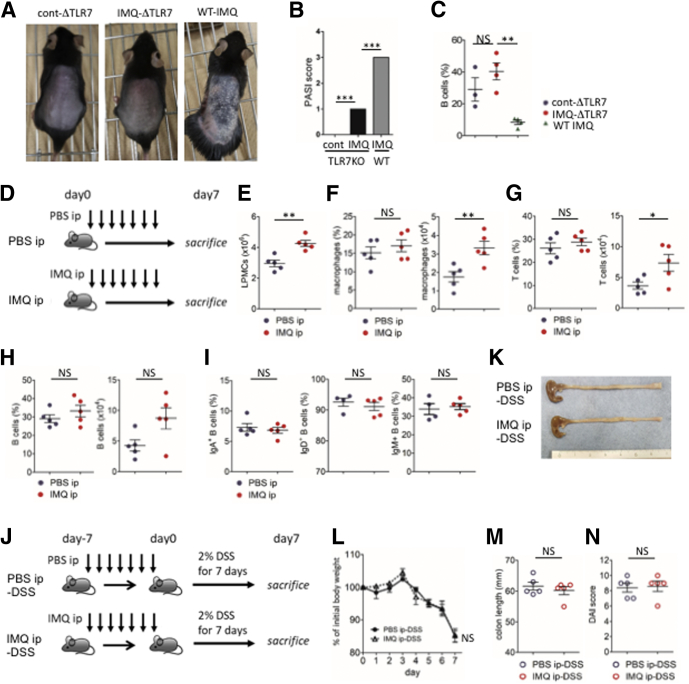
Figure 4.
Psoriasis-like dermatitis was required to induce immunologic changes in the gut and to exacerbate DSS colitis. (A–C) Psoriasis-like dermatitis was induced by topical IMQ treatment in TLR7-/- mice (IMQ-ΔTLR7 mice) and WT mice (WT-IMQ mice). As control, vehicle was applied to TLR7-/- mice (cont-ΔTLR7 mice) instead of IMQ, and the severity of dermatitis and B cell change in colonic lamina propria were assessed. Skin appearance after induction of psoriasis-like dermatitis by (A) IMQ, (B) Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score, and (C) the percentage of B cells in colonic lamina propria analyzed by flow cytometry. (D–I) IMQ was injected IP to mice daily for a week and lymphocytes in colonic lamina propria were analyzed. PBS was injected instead of IMQ as control. (D) Experimental protocol, (E) absolute number of lamina propria mononuclear cells (LPMCs), (F) percentage in CD45+lineage- cells (left) and absolute number (right) of macrophages in colonic lamina propria, (G) percentage in CD45+ cells (left) and absolute number (right) of T cells, and (H) B cells. (I) Percentages in the total B cells of IgA+ B cells, IgD+ B cells, and IgM+ B cells. (J) Experimental protocol. Mice injected IP with IMQ or PBS were further administered 2% (wt/vol) DSS for 7 days to induce colitis, and the severity of colitis was assessed. (K) Representative photograph of colon on day 7 of DSS colitis. (L) Body weight change during DSS administration. (M) Colon length on day 7 of DSS colitis. (N) DAI score on day 7 of DSS colitis. Each symbol represents an individual mouse (n = 3–5). Statistical analyses were performed with the Student t test. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .005. Error bars represent the SEM of samples within a group. Lineage, CD3, CD19, B220, and NK1.1.