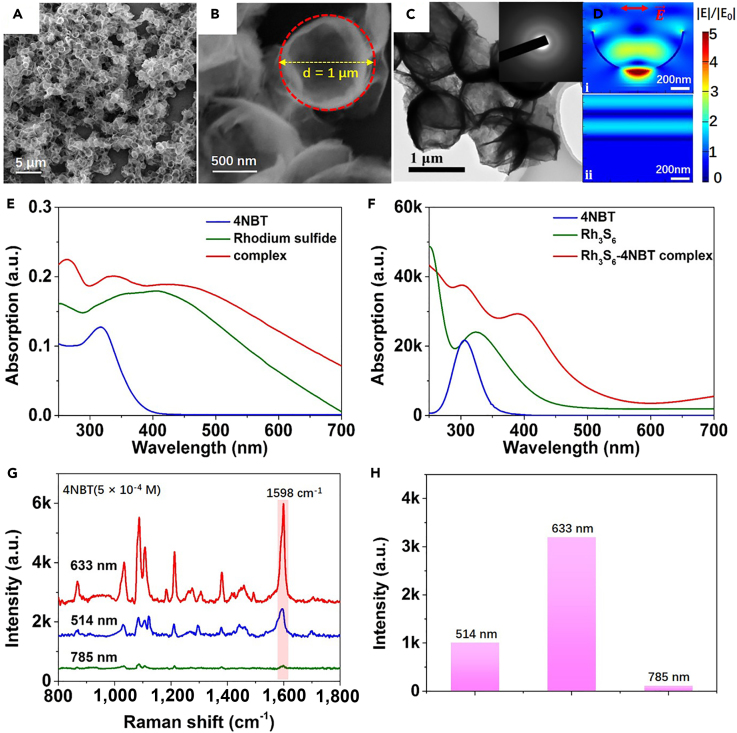
Figure 3.
Characterization and SERS Response of Amorphous Rhodium Sulfide Microbowls
(A and B) Scanning electron microscopic images of amorphous rhodium sulfide microbowls with different magnifications.
(C) Transmission electron microscopic images of the amorphous rhodium sulfide microbowls with selected area electron diffraction pattern shown in inset.
(D) Calculated electric field distributions (|E|/|E0|) for (i) amorphous rhodium sulfide microbowl with 1 μm diameter and 20 nm thickness and (ii) amorphous rhodium sulfide film with 20 nm thickness.
(E) Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra of 4NBT, rhodium sulfide, and rhodium sulfide-4NBT complex in ethanol.
(F) Time-dependent density functional theory-calculated absorption spectra of a 4NBT, Rh3S6, and Rh3S6-4NBT complex in ethanol.
(G and H) SERS spectra (G) and Raman intensities of the 1,598 cm−1 mode (H) for 4NBT (5 × 10−4 M) adsorbed on the amorphous rhodium sulfide microbowls at different incident wavelengths.
See also Figures S3–S5.