Fig. 2.
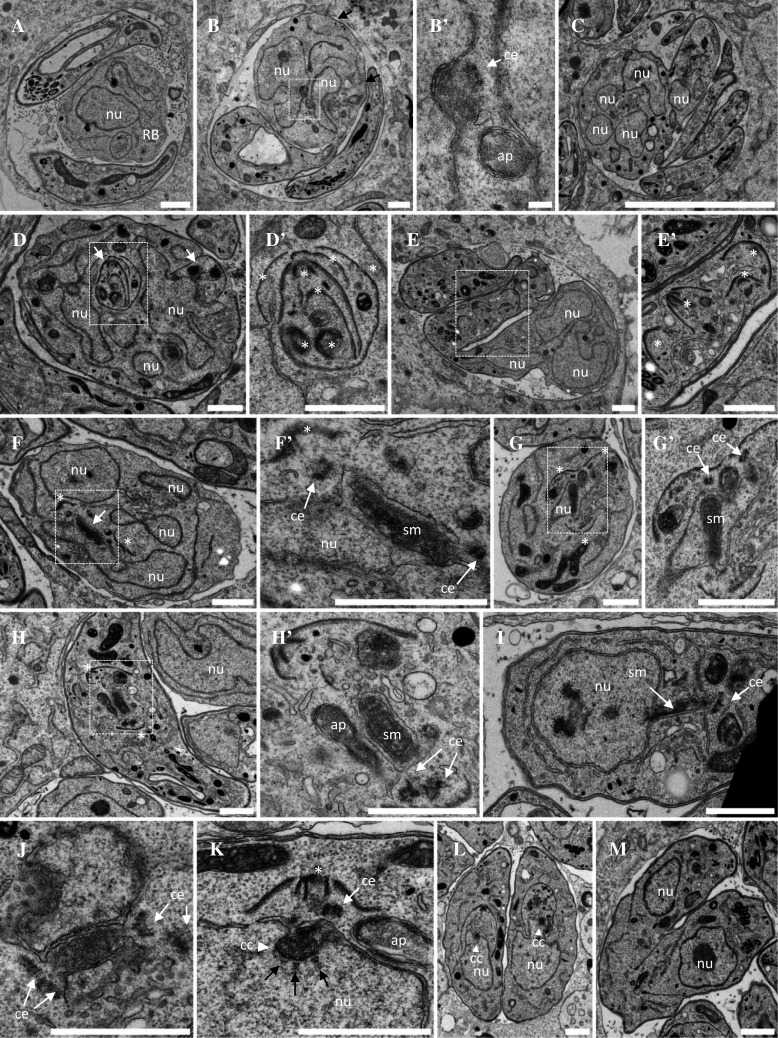
Ultrastructural analysis of ark1D/A-Δku80 dominant negative mutant parasites. a–e′ Representative electron micrographs of parasites treated during 12 h with shield-1 to stabilize the expression of the DD-Myc-TgArk1D/A protein. Parasites showed catastrophic division defects. a Vacuole showing a large residual body containing a nucleus and various organelles. Two parasites show cytoplasmic and apical organelles and large aberrant electron lucent vacuoles but no apparent nucleus. b A parasite shows discontinuous IMC stretches under the plasma membrane (black arrows) and two nuclei in one of which a centriole next to a depression of the nuclear envelope suggests an early step of spindle formation. Higher magnification in b′. c Monster cell showing multiple nucleus sections and three nucleus free tachyzoites. d Monster cell showing multi-lobed nucleus and multiple daughter inner membrane complexes (IMC, white arrows). A detail shown at higher magnification in d′ shows several IMCs nested like Russian dolls (white asterisk). e, e′ Monster cell showing multi-lobed nucleus and some cytoplasmic organelles, connected to another IMC-coated compartment containing multiple daughter apical complexes randomly organized (white asterisks in the enlarged area e′) and various organelles but no apparent nucleus. f Residual body containing several nuclei, one of which harboring a nuclear envelope-bounded funnel containing spindle microtubules (White arrow and enlargement in f′). At both ends of the funnel a centriole is found, associated with a daughter IMC (white asterisks). g Parasite containing multiple daughter IMCs. The nucleus is traversed by a funnel containing spindle microtubules (higher magnification in g′). h, h′ Parasite showing two apical buds (white asterisks) at both ends of a spindle surrounded by a double membrane, but no nucleus can be seen on the same section. i Parasite showing a nucleus harboring a membranous funnel stretched out of the nucleus, containing spindle microtubules. Centrioles are present at the extremity of the funnel. j–m DD-Myc-TgArk1WT-expressing parasites grown in the presence of shield-1. j A funnel containing spindle microtubules is transiently observed after centriole duplication, and before the assembly of daughter cells apical complexes. k Later during mitosis, the mitotic spindle poles turn into centrocones (white arrowhead) with kinetochores aligned next to their base (black arrows). The daughter apical complex has started to assemble (white asterisk). l Early steps of cytokinesis by endodyogeny. Nuclei are pulled inside the body of the assembling daughter cells. m Late stages of cytokinesis. Daughter cells emerging from the body of the mother. All the steps described from J to M are similar to the ones observed in wild-type untreated parasites. nu nucleus, ap apicoplast, ce centriole, sm spindle microtubule, rb residual body. Scale bar = 1 µm
