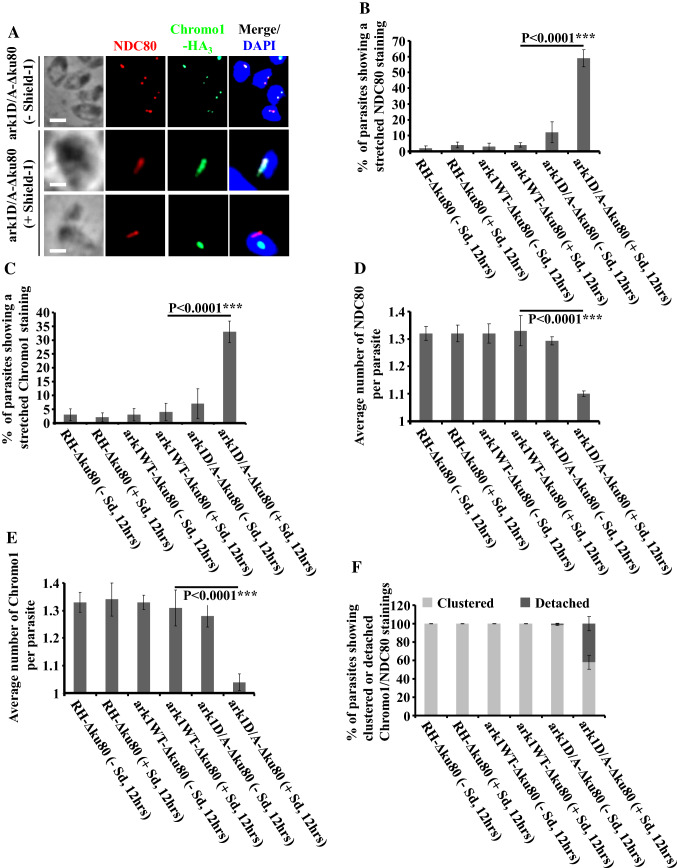
Fig. 5.
Interfering with TgArk1 function decreasingly affects the duplication of kinetochores and centromeres and their clustering. a Co-staining of TgNDC80 (a kinetochore marker, red dots) and TgChromo1-HA3 (a centromere marker, green dots) shows under-duplication of both subcellular structures and their detachment in the ark1D/A-Δku80 strain treated with shield-1 (lower panels). The ark1D/A-Δku80 strain in the absence of shield-1 (top panel) shows a normal pairing of kinetochore/centromere per nucleus (two kinetochore clusters/two centromeres). The nuclei are stained with DAPI (in blue). Scale bars represent 2 μm. b, c Quantification of the number of parasites showing a stretched kinetochore or centromere in three different strains (RH-Δku80, ark1WT-Δku80 and ark1D/A-Δku80) in the presence or absence of shield-1 for 12 h. At least 900 parasites were examined for each condition. Values are mean ± SD for three independent experiments. d, e The average of TgNDC80 containing kinetochores or TgChromo1-HA3 containing centromeres per parasite was quantified in 900 parasites revealing a significant reduction of the kinetochores and centromeres when ark1D/A-Δku80 parasites were treated in the presence of shield-1 (red and green dots). Values are mean ± SD for three independent experiments. f Quantification of the number of parasites showing clustered or detached kinetochore/centromere pairing in three different strains (RH-Δku80, ark1WT-Δku80 and ark1D/A-Δku80) in the presence or absence of shield-1 for 12 h. At least 900 parasites were examined for each condition. Values are mean ± SD for three independent experiments