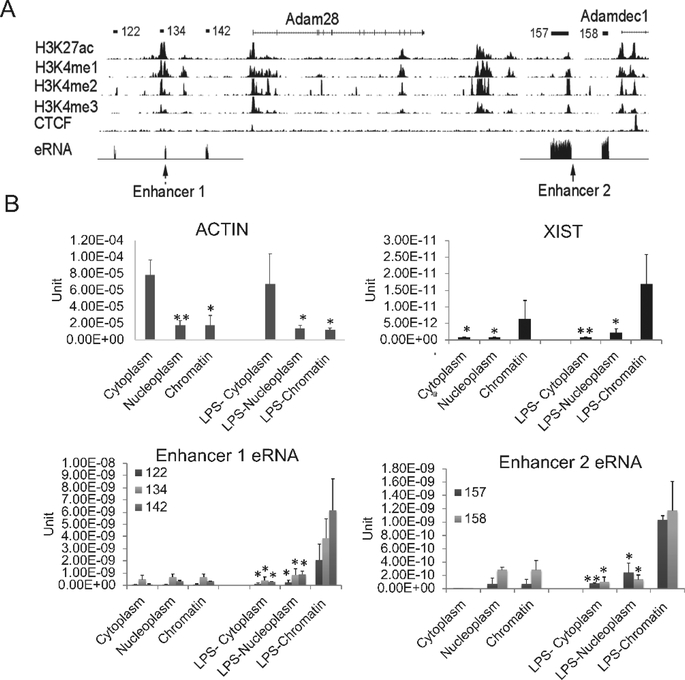
Figure 2. The characterization of identified enhancer RNAs.
(A) The UCSC genome browser view shows the position of ADAM family genes and enhancers. The detailed annotation of the eRNAs was identified by the Tophat-Cufflinks pipeline in human SLE monocytes (Shi et al., 2014). The eRNAs are shown schematically a the top of the figure and the eRNA tracks from our RNA-seq dataset are displayed in the eRNA track with the mRNAs removed due to the magnitude of their expression compared to the eRNAs. Histone marks in human CD14+ monocytes from the ENCODE data indicated that these eRNAs are located within active enhancer regions, termed Enhancer 1 and Enhancer 2. (B) The eRNAs were localized primarily to the chromatin fraction. RNA was extracted from MonoMac6 cytoplasm, nucleoplasm and chromatin fractions with or without 1μg/ml LPS treatment. qRT-PCR was performed. Actin B and XIST are shown as positive controls for cytoplasmic and chromatin fractions, respectively (n=3, error bars in panels denote SD). Symbols indicate statistical significance: * indicates p<0.05, ** p<0.01.