Figure 1: The binding mode and chemical structure of NS3/4A protease inhibitors.
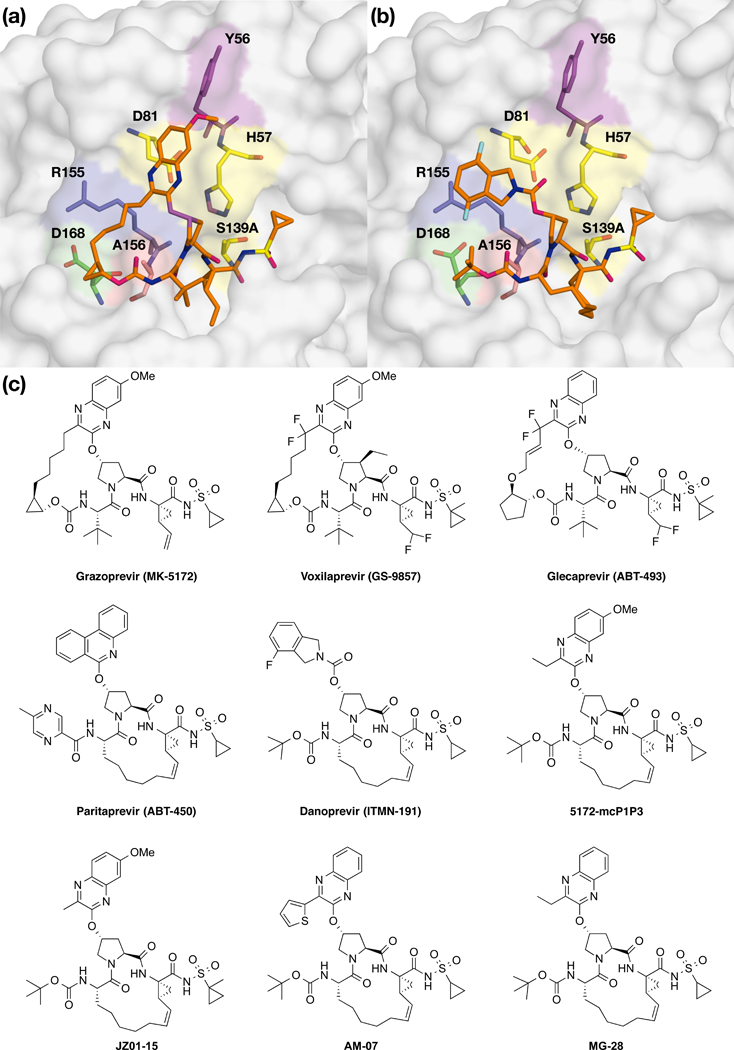
Surface view of NS3/4A protease inhibitors (a) grazoprevir and (b) danoprevir bound to the active site. Danoprevir’s P2 isoindoline moiety occupies two conformations in the protease active site. The catalytic triad is shown in yellow and drug resistance residues Tyr56, Argl55, Ala156, and Asp 168 are shown in magenta, blue, red and green, respectively. Residues Tyr56 and Asp 168 are located almost 15 Å apart in the protease active site, (c) Grazoprevir, voxilaprevir, glecaprevir and paritaprevir are approved by the FDA. Danoprevir was in clinical development. All other inhibitors were synthesized in house as P1-P3 macrocyclic analogs of grazoprevir.
