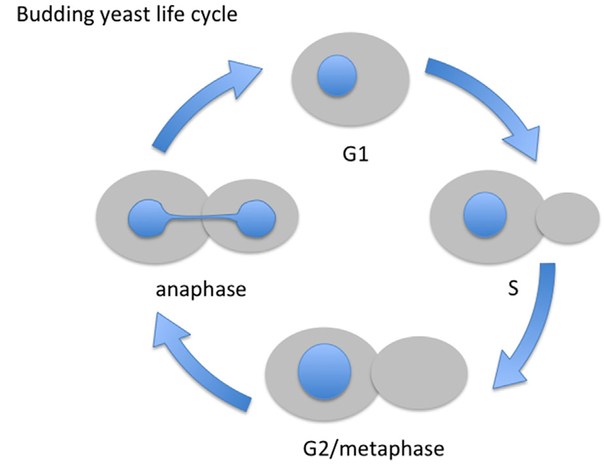
Fig. 1.
The budding yeast life cycle. The cell cycle of budding yeast can be followed by bud size and nuclear shape (in blue). Cells are born in G1 without a bud. As the cell reaches a critical size it initiated DNA replication (S phase) and a bud forms. The bud continues to grow as cells traverse G2 and reach metaphase. At the metaphase to anaphase transition one copy of each of the sister chromatids begins to segregate to the bud (not shown) and the anaphase nucleus elongates to accommodate this segregation.