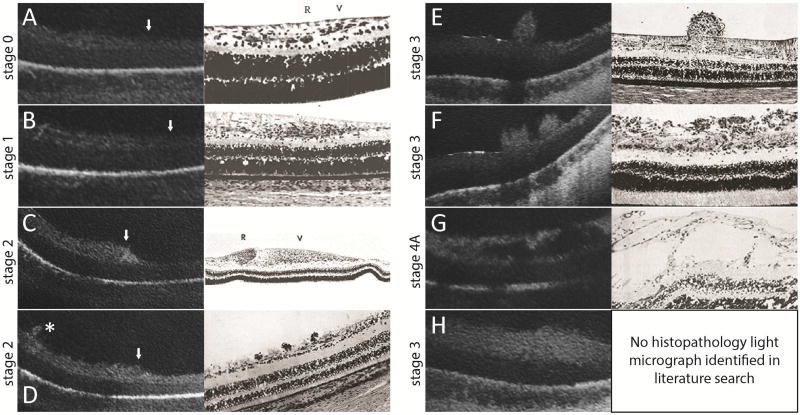
Figure 3.
SDOCT images (left) are correlated with historic representative light micrographs (right) at the vascular-avascular junction (A–D, white arrowhead with vascularized retina on the left side of the images) or adjacent to the vascular-avascular junction (E–G, posterior, and H, anterior) in eyes with ROP. A: Stage 0 ROP: in vascularized retina a faint hyporeflective band divided the inner retinal hyperreflective layer which gradually tapered to a single hyperreflective band in avascular retina. This was comparable to the normal angiogenesis pattern reported by Foos31 (adapted image), although the retinal layers were not as evident on OCT imaging compared to histopathology studies. B: Stage 1 ROP: a similar three-layered inner retina on the left gradually tapered to a one-layered structure in avascular retina. Similar to Foos31, the total thickness of the vascularized retina appeared to be greater than in stage 0 ROP.31 (also see Supplementary Table 1 thicknesses) C: Stage 2 ROP: pronounced thickening at the vascular-avascular junction was consistent with the ridge structure with hypertrophied anterior vanguard and posterior rear guard cells reported by Foos31. As with all OCT imaging, specific cellular elements could not be distinguished. D: Small neovascular buds, not noticed on clinical examination, could be seen on OCT in stage 2 ROP (asterisk). This was similar to the small elevations on the retinal surface observed by Reese,28 which were presumed to be early endothelial proliferation. E, F: Stage 3 ROP: neovascular buds (E) and bands (F) frequented the preretinal surface. Their configurations were also consistent with neovascular findings reported by Reese.28 G: Stage 4A ROP: there were schisis-like changes in the inner retinal layers posterior to the presumed area of retinal detachment. These schisis-like changes were often cavitary, and appeared similar to the large cystic spaces in the nerve fiber layer in later stages of proliferative disease reported by Kushner.33 H: In stage 3 or 4 ROP, there was often diffuse thickening of the inner retinal layer of avascular retina. No correlating histopathology light micrograph was identified in our literature search.