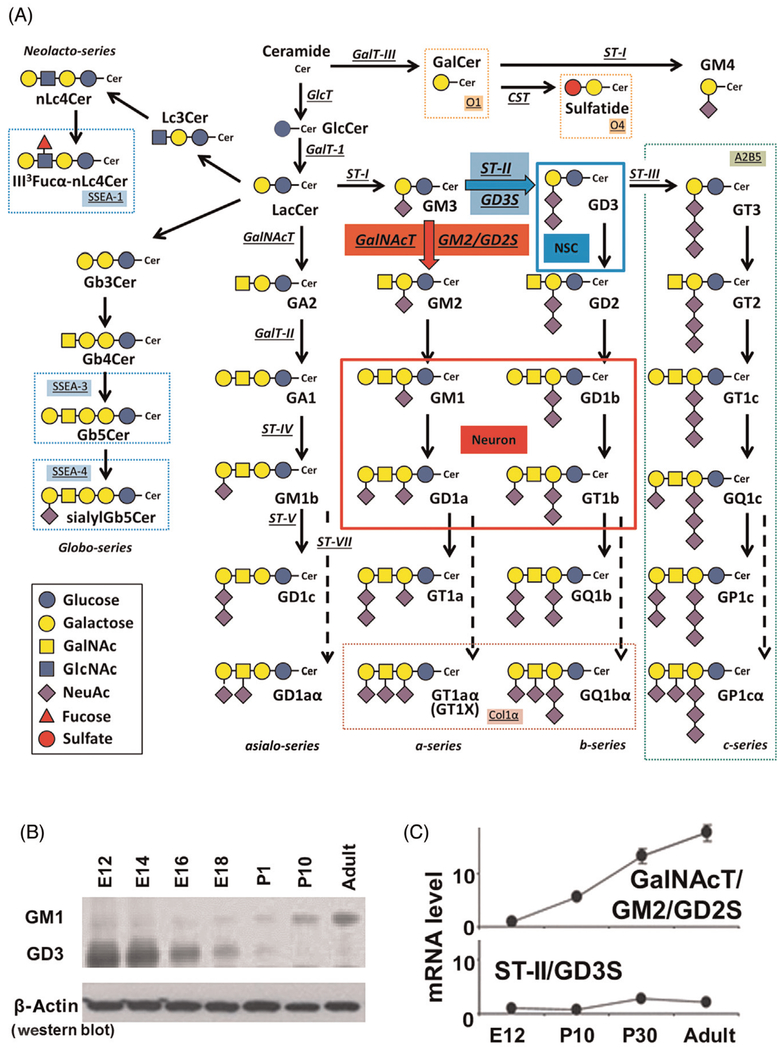
Fig. 1.
Glycosphingolipids and glycosyltransferases in the nervous system. (A) Structures and biosynthetic pathways of glycosphingolipids (GSLs). Cer, Ceramide; CST, cerebroside sulfotransferase (Gal3st1, sulfatide synthase); GalNAc-T, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase I (B4galnt1, GA2/GM2/GD2/GT2-synthase); GalT-I, galactosyltransferase I (B4galt6, lactosylceramide synthase); GalT-II, galactosyltransferase II (B3galt4, GA1/GM1/GD1b/GT1c-synthase); GalT-III, galactosyltransferase III (Ugt8a, galactosylceramide synthase); GlcT, glucosyltransferase (Ugcg, glucosylceramide synthase); ST-I, sialyltransferase I (St3gal5, GM3-synthase); ST-II, sialyltransferase II (St8Sia1, GD3-synthase); ST-III, sialyltransferase III (St8Sia3, GT3-synthase); ST-IV, sialyltransferase IV (St3gal2, GM1b/GD1a/GT1b/GQ1c-synthase); ST-V, sialyltransferase V (St8sia5, GD1c/GT1a/GQ1b/GP1c-synthase); ST-VII, sialyltransferase VII (St6galnac6, GD1aα/GT1aα/GQ1bα/GP1cα-synthase). Official symbols of genes are represented in italics in this figure legend. GD3 is the most abundant ganglioside in rodent NSCs. c-Series gangliosides are A2B5 antigens. GM1, GD1a, GD1b, and GT1b are the most abundant ganglioside species in adult mammalian brain and neurons. Oligodendrocyte markers O1 and O4 are GalCer and sulfatide, respectively. GT1aα and GQ1bα are cholinergic-specific antigens (Chol-1α). (B) Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and (C) quantitative PCR studies demonstrate the structural complexity of gangliosides that develops with age. Note the dynamic changes from E12 up through the adult for expression of gangliosides (GM1 and GD3) and glycosyltransferases (GalNAcT; GD2/GM2S and ST-II; GD3S), indicative of developmental regulation.