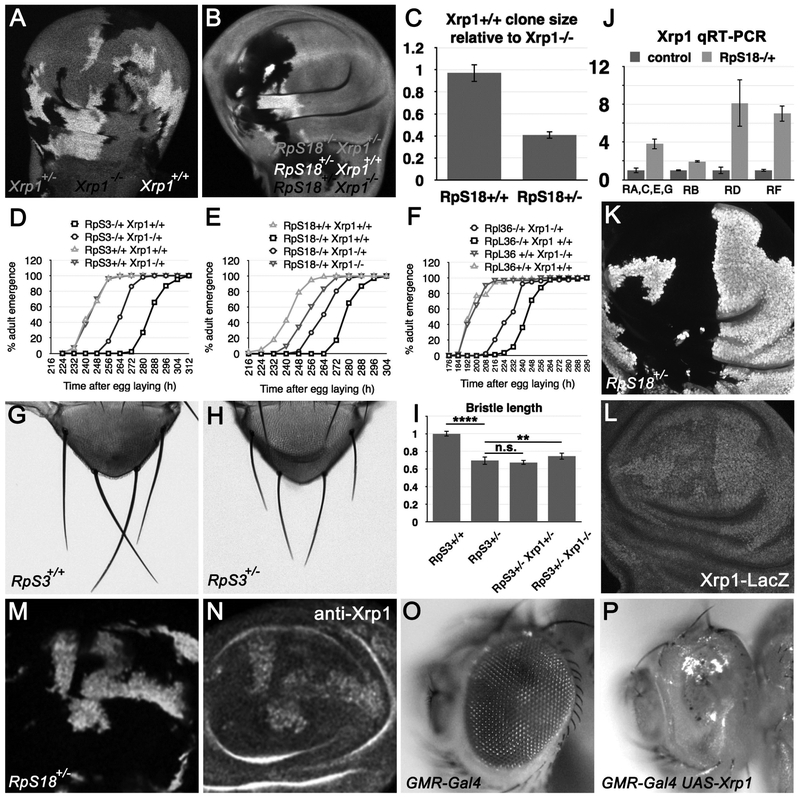
Figure 3. Xrp1 expression retards growth.
A) Xrp1+/− wing discs containing clones of Xrp1−/− and Xrp1+/+ cells. B) RpS18+/− Xrp1+/− wing discs containing clones of RpS18+/− Xrp1−/− and RpS18+/− Xrp1+/+ cells. C) Quantification of clones size data from experiments illustrated in panels A,B. D-F) Graphs representing developmental rate as time in hours from egg laying to adult emergence for the genotypes indicated. In panel D, the emergence times for RpS3+/+ Xrp1+/+ and RpS3+/+ Xrp1+/− were not significantly different (two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, p=0.542). In panel F, the emergence times for RpL36+/+ Xrp1+/+ and RpL36+/+ Xrp1+/− were not significantly different (two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, p=0.43). In panels D-F, the emergence of RpS3++/−, RpS18+/−, and RpL36+/− was each delayed significantly compared to the wild type controls (one-tailed Mann-Whitney test, p<0.00001 in all cases). The rescue of the respective Rp+/− Xrp1+/− adults was highly significant (one-tailed Mann-Whitney test, p<0.00001 in all cases). In panel E, the accelerated development of RpS18+/− Xrp1−/− compared to RpS18+/− Xrp1+/− was highly significant (significant (one-tailed Mann-Whitney test, p<0.00001) G) Scutellum of RpS3+/+ fly, showing the scutellar bristles. H) Scutellum of RpS3+/− fly, showing the scutellar bristles. See Figure S2 for more genotypes. I) Mean length of posterior scutellar bristles from genotypes indicated. RpS3+/− bristles were ~30% shorter than controls (p<0.0001, t-test). RpS3+/− Xrp1+/− bristles were no different. RpS3+/− Xrp1−/− bristles were slightly longer (~5%) and this difference was statistically significant (p<0.01, t-test). J) qRT-PCR measurements of Xrp1 transcript isoforms (see Figure 1A for diagram of isoforms). All the Xrp1 transcripts were elevated in RpS18+/− wing imaginal discs in comparison to wild type controls. See Figure S2 for qRT-PCR data compared to tubulin mRNA levels. K) Mosaic wing disc containing RpS18+/− cells (labeled for ubi-GFP) and RpS18+/+ cells (unlabeled). L) Xrp1-LacZ labeling of the wing imaginal disc shown in panel K. Since the LacZ mRNA encoded by the enhancer trap insertion contains no sequences from Xrp1, elevated LacZ labeling likely reflects enhanced transcription. M) Mosaic wing disc containing RpS18+/− cells (labeled for ubi-GFP) and RpS18+/+ cells (unlabeled). N) Anti-Xrp1 labeling of the wing imaginal dsc shown in panel M. O) Flies heterozygous for the GMR-Gal4 transgene had normal eyes. P) Ectopic Xrp1 expression under control of the GMR-Gal4 driver ablated the eye almost completely(Tsurui-Nishimura et al., 2013). Supplemental data related to this Figure is shown in Figure S3 and Table S1.