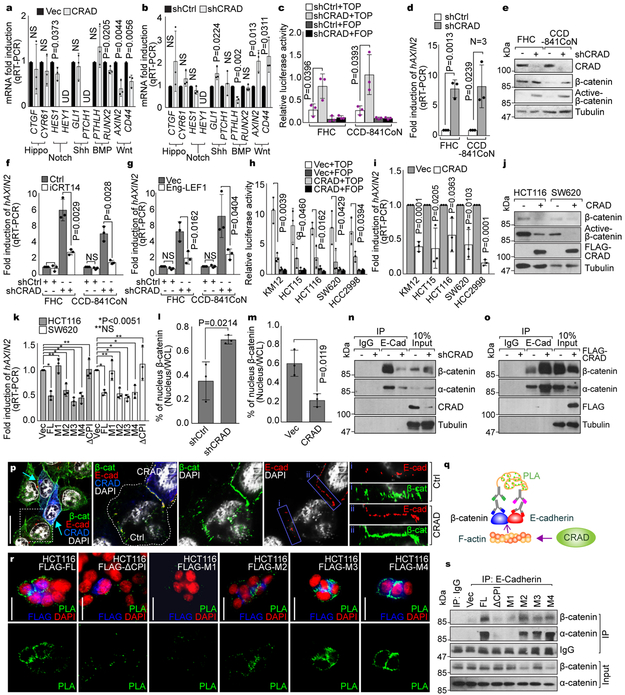
Figure 3. Loss of CRAD-activated Wnt signaling by disrupting CCA complex.
a, Decreased Wnt signaling target genes by CRAD. 24hr after transfection, HCT116 cells were analyzed for qRT-PCR.
b, Increased Wnt signaling target genes by CRAD knockdown. CRAD-depleted CCD-841CoN cells were analyzed for qRT-PCR.
c and d, Increased β-catenin transcriptional activity by CRAD depletion. IECs were transfected with β-catenin reporter plasmids (TOP/FOPFLASH) for luciferase assays (c). qRT-PCR for AXIN2 (d).
e, Increased β-catenin protein by CRAD depletion in IECs. IB assays.
f and g, Inhibition of CRAD depletion-induced AXIN2 upregulation by iCRT14 (f) or Eng-LEF1 (g). 24hr after iCRT14 (an inhibitor of β-catenin-TCF binding; 100μM) treatment or Eng-LEF1 (a dominant-negative mutant blocking β-catenin-mediated gene activation) transient transfection, IECs were analyzed for qRT-PCR.
h-j, Suppression of β-catenin transcriptional activity by CRAD in CRC cells. 24hr after transfection, CRC cells were analyzed for TOP/FOPFLASH luciferase analysis (h), qRT-PCR of AXIN2 (i), and IB for β-catenin (j). Experiment performed once.
k, The inhibition of β-catenin target gene expression by CPI motif-containing CRAD mutants. 24hr after transfection, CRC cells were analyzed for TOP/FOPFLASH luciferase activity.
l, Decreased nuclear β-catenin by CRAD. IECs (l) and CRC cells (m) were transfected with shCtrl or shCRAD and Vec or CRAD, respectively. After 48hr, cells were fractionated into the cytosolic and nucleus fractions, followed by IB. Quantification of nucleus β-catenin was assessed using ImageJ.
n, Decreased interaction between E-cadherin and catenins by CRAD depletion. Co-IP assays of shCRAD-CCD-841CoN. The representative images are shown from three independent experiments with similar results.
o and p, Increased interaction between E-cadherin and catenins by CRAD. HCT116 cells were transfected with FLAG-CRAD plasmid. Co-IP assays (o) and IF staining (p). Arrows indicate CRAD-expressing cells. Compared to i (non-transfected cells), ii (CRAD-expressing cells) displays the increased colocalization of E-cadherin and β-catenin by CRAD. The representative images are shown from three independent experiments with similar results.
q, Illustration of E-cadherin-β-catenin binding analysis using Duolink assays.
r and s, Restoration of E-cadherin-β-catenin binding by CPI motif-containing CRAD mutants in CRC cells. Duolink assay (r). Green (PLA) fluorescence indicates E-cadherin-β-catenin interaction. Co-IP analysis (s).
Representative images of three experiments with similar results; Scale bars indicate 20μm; Data in panels a-h and k-m are from n=3 independent experiments; Error bars: mean ± S.D.; NS: not significant (P>0.05); Two-sided unpaired t-test;