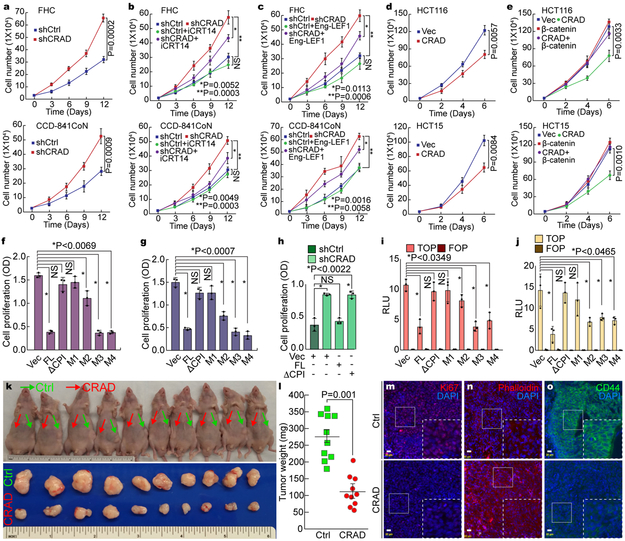
Figure 4. Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation by CRAD.
a, IEC hyperproliferation by CRAD depletion. The proliferation of FHC and CCD-841CoN cells (shCtrl [control] and shCRAD) were analyzed by cell counting.
b and c, Suppression of shCRAD-induced cell hyperproliferation by β-catenin inhibition in IECs. FHC and CCD-841CoN (shCtrl and shCRAD) cells were treated with iCRT14 (100μM) for 14 days, and cell number was counted (b). IECs (shCtrl and shCRAD) were transfected with Eng-LEF1 and analyzed for cell proliferation (c).
d, CRC cell growth inhibition by CRAD expression. HCT116 and HCT15 cells (Vec [control] and CRAD expressing) were analyzed for cell proliferation.
e, β-catenin rescues CRAD-induced CRC cell growth inhibition. HCT116 and HCT15 cells were transfected with CRAD or β-catenin plasmids and analyzed for cell proliferation.
f-h, CRC cell growth inhibition by CPI motif-containing CRAD mutants. CRAD (FL, ΔCPI, and M1-M4)-transfected CRC cells were analyzed for cell proliferation. HCT116 (f); SW620 cells (g). CCD-841CoN cells were transfected with each plasmid and analyzed for cell proliferation (h).
i and j, Suppression of β-catenin reporter by CPI motif-containing CRAD mutants. HCT116 (i) and SW620 (j) cells transfected with CRAD FL or mutant constructs were analyzed for luciferase activity.
k-o, Inhibition of ex vivo tumor development by CRAD. HCT116 (control [Ctrl]) and HCT116-CRAD cells were subcutaneously injected into the left flank (control; green arrows; k) and the right flank (CRAD-expressing; red arrows; k), and analyzed for tumor weight (l; n=10 mice) and IHC (m-o); Ki67 (m); Phalloidin (n); CD44 (o). These experiments (k and l) were performed once.
Scale bars indicate 20μm; Data in panel a-j and o are from n=3 independent experiments; Error bars: mean ± S.D.; NS: not significant (P>0.05); Two-sided unpaired t-test.