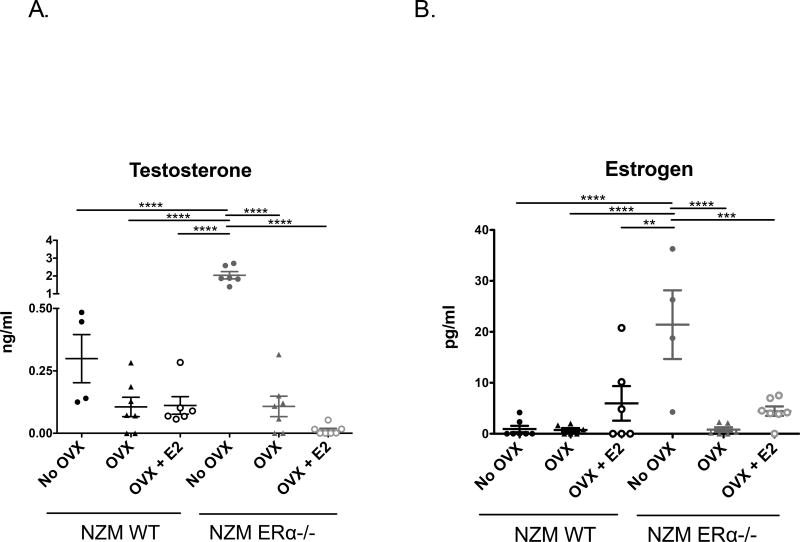
Figure 2. Hormone levels in NZM2410 WT and NZM ERα−/− mice +/− OVX and E2-repletion.
All mice were female. A) Serum testosterone (T2) levels where determined by radioimmunoassay and ELISA. Intact NZM ERα−/− mice had the highest levels of T2 due to known hypergonadism, and were significantly increased over all groups, including intact NZM WT mice. B) Estrogen (E2) levels in serum samples were assessed via ELISA. A subset of NZM WT and NZM ERα−/− mice had E2 replaced via subcutaneous 90d sustained-release pellet after OVX (implanted twice). Intact NZM ERα−/− mice had significantly higher levels of E2 (although not technically supraphysiologic), even more than those that were E2-repleted.