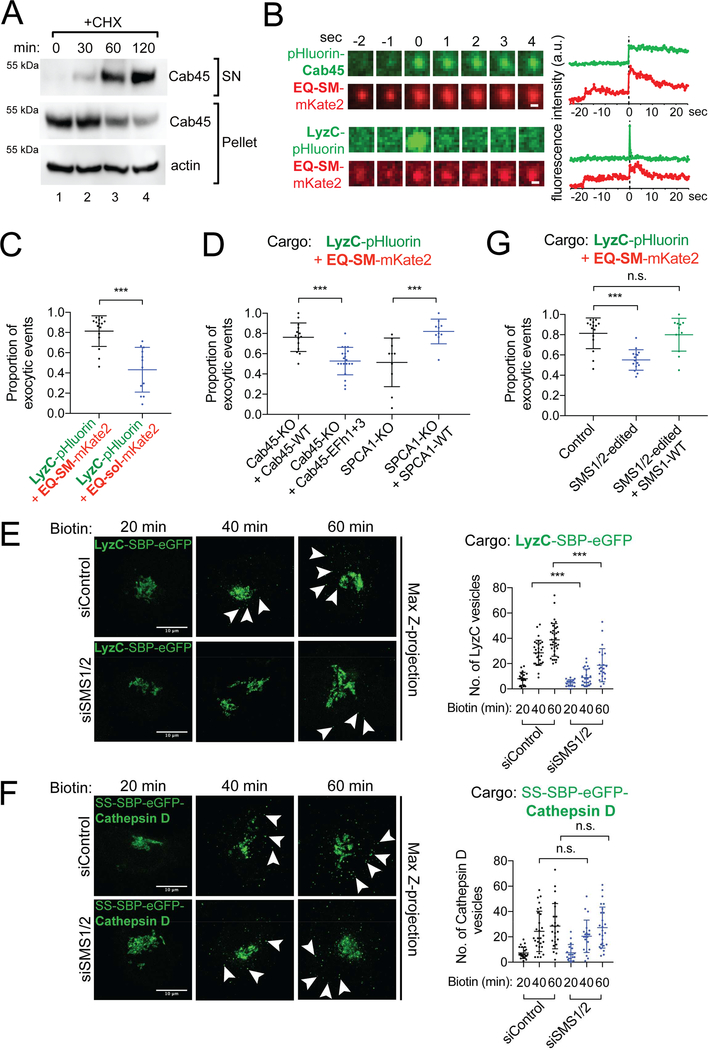
Figure 4. Cab45, LyzC, and EQ-SM are exocytosed via the same vesicles in a sphingomyelin synthesis dependent manner.
(A) Cell culture supernatants and whole cell lysates of HeLa cells were collected after 0, 30, 60 and 120 min incubation with cycloheximide (CHX) and probed for Cab45 by immunoblotting. (B) Time-lapse gallery of Cab45, LyzC, and EQ-SM exocytosis. Galleries show example exocytic events of pHluorin-Cab45 or LyzC, and EQ-SM-mKate2 captured by TIRFM. The corresponding graphs show the summed fluorescence intensities for each frame in each channel over time. (C) LyzC is co-sorted with EQ-SM, but not EQ-sol, into exocytic vesicles. The mean proportions of exocytic events observed in 3 independent experiments (± s.d.) where LyzC-pHluorin containing vesicles also released mKate2-tagged EQ-SM or EQ-sol are indicated (362 events/15 cells for LyzC+EQ-SM and 268 events/12 cells for LyzC+EQ-sol). (D) Cab45 EFh1 and EFh3 and SPCA1 are required for cosorting of LyzC and EQ-SM. Genome edited Cab45 null cells expressed Cab45-WT or Cab45EFh1+3-mut by transfection or genome edited SPCA1 null cells that expressed or did not express SPCA1-WT by transfection. The cargo loads of exocytic vesicles were determined as described for (B). The means (± s.d.) are shown for n=239 events/14 cells for Cab45-WT, n=128 events/10 cells for Cab45-EFh1+3, n=163 events/10 cells for SPCA1-KO, n=157 events/10 cells for SPCA1-WT. (E) Depletion of sphingomyelin synthases (SMS1 and SMS2) delays export of LyzC-SBP-eGFP from the Golgi apparatus. HeLa cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting SMS1 and SMS2 or non-targeted control for two days prior to transfection with a plasmid that directs expression of LyzC-SBP-eGFP and the Streptavidin-KDEL ‘anchor’. The number of cytoplasmic vesicles per cell was determined at the indicated time points after release of LyzC-SBP-eGFP from the ER by addition of biotin. Arrowheads point to cytoplasmic vesicles. Bars, 10 μm. Vesicle counts (mean ± s.d.) from at least 18 cells per condition in 3 independent experiments are plotted in the graph on the right. (F) Depletion of SMS1 and SMS2 does not delay export of SS-SBP-eGFP-Cathepsin D vesicles from the Golgi apparatus. Arrowheads point to cytoplasmic vesicles. Assays were conducted as in (A). Bars, 10 μm. Vesicle counts from at least 18 cells per condition in 3 independent experiments are plotted (mean ± s.d.). (G) TIRF microscopy-based sorting assays were used to determine the proportion of LyzC-pHluorin exocytic vesicles that also contained EQ-SM-mKate2 (mean ± s.d.) in genome edited HeLa cells (SMS1/2-edited) that express SMS1 and SMS2 at reduced levels. See also Figure S3.