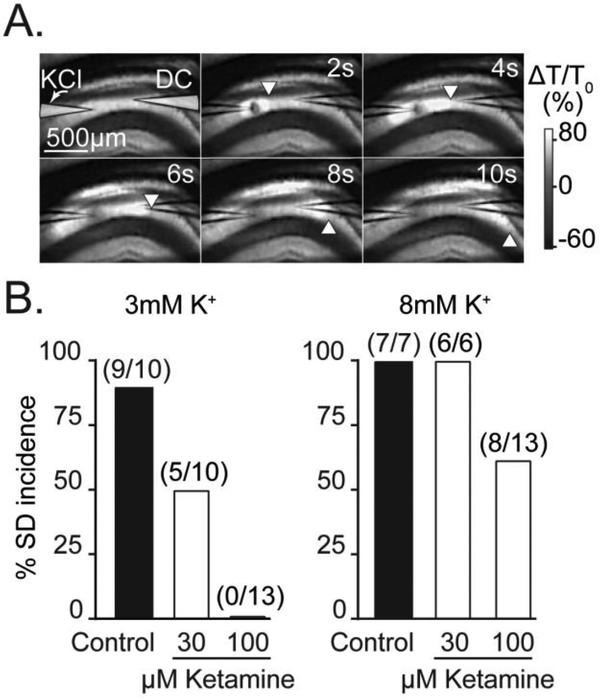
Figure 1. Basal extracellular K+ influences sensitivity to ketamine.
A: Representative intrinsic optical signals showing SD propagation through the hippocampal CA1 region of a brain slice. SD was triggered by micro injection of KCl from a micropipette on the left (labeled “KCl”) and SD is visualized as a slowly-propagating wave of increased light transmission. The location of the advancing wavefront is marked by white arrowheads and a second microelectrode (labeled “DC”) was used to confirm electrical responses of SD coincident with arrival of the optical signal (not shown). The upper right-hand values indicate time, in seconds, relative to the triggering of the KCl stimulus pulse. B: Effect of ketamine exposures on SD incidence under two different recording conditions (3mM vs 8mM bathing K+). Ketamine more potently prevented SD incidence in the lower basal K+ recording conditions. Values in parenthesis indicate number of preparations.