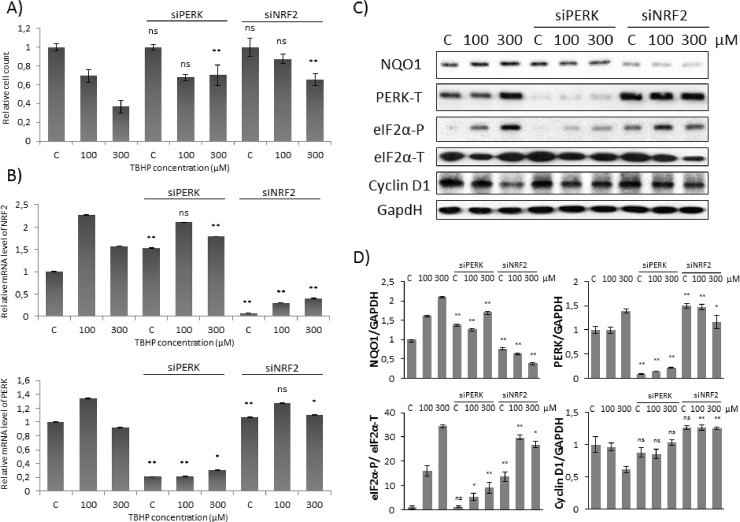
Fig 2. Cyclin D1 degradation is not observed at early stage of low level of oxidative stress.
Concentration dependency of oxidative stress treatment was followed with/without a background of PERK or NRF2 silencing. HEK293T cells were cultured with 100 or 300 μM TBHP for 1.5 hours, while NRF2 or PERK gene expression was depleted by NRF2 or PERK siRNA. (A) The relative amount of viable HEK293T cells. (B) The efficiency of NRF2 (upper panel) and PERK (lower panel) silencing was checked on mRNA level. The mRNA level was followed by real-time PCR. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping gene. The intensity of NRF2 is normalised for GAPDH. (C) During oxidative stress the markers of NRF2 (NQO1), PERK (PERK-T, eiF2α -P) and Cyclin D1 were followed by immunoblotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (D) Densitometry data represent the intensity of NQO1, PERK-T and Cyclin D1 normalised for GAPDH and eiF2α-P normalized for total level of eiF2α. For each of the experiments, three independent measurements were carried out. Error bars represent standard deviation; asterisks indicate statistically significant difference from the control: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.