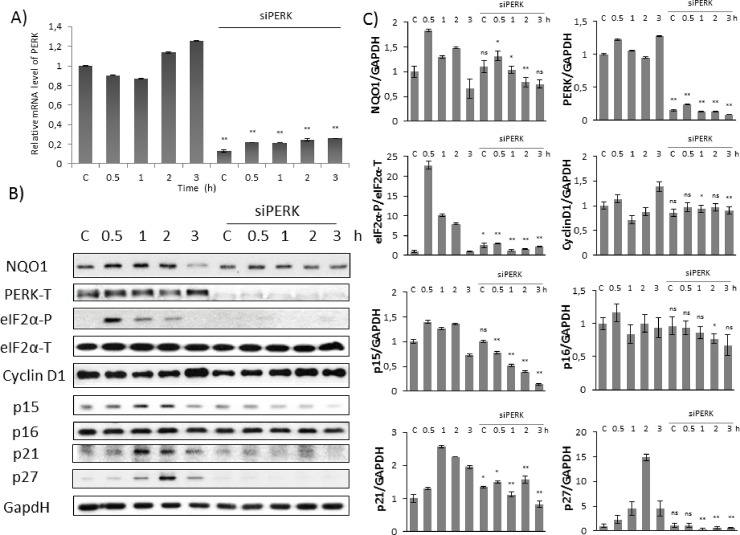
Fig 3. Silencing of PERK down-regulates Cyclin D1 inhibitors at early stage of oxidative stress.
Time dependency of oxidative stress treatment was followed with/without a background of PERK silencing. HEK293T cells were cultured with TBHP for 0.5-1-2-3 hours, while PERK gene expression was depleted by PERK siRNA. (A) Testing the effectiveness of RNA silencing. PERK mRNA level was followed by real-time PCR in cell culture containing PERK siRNA. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping gene. The intensity of PERK is normalised for GAPDH. (B) During oxidative stress the markers of NRF2 (NQO1), PERK (PERK-T, eiF2α -P), Cyclin D1 and its inhibitors (p15, p16, p21, p27) were followed by immunoblotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (C) Densitometry data represent the intensity of NQO1, PERK-T, Cyclin D1, p15, p16, p21 and p27 normalised for GAPDH and eiF2α-P normalized for total level of eiF2α. For each of the experiments, three independent measurements were carried out. Error bars represent standard deviation; asterisks indicate statistically significant difference from the control: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.