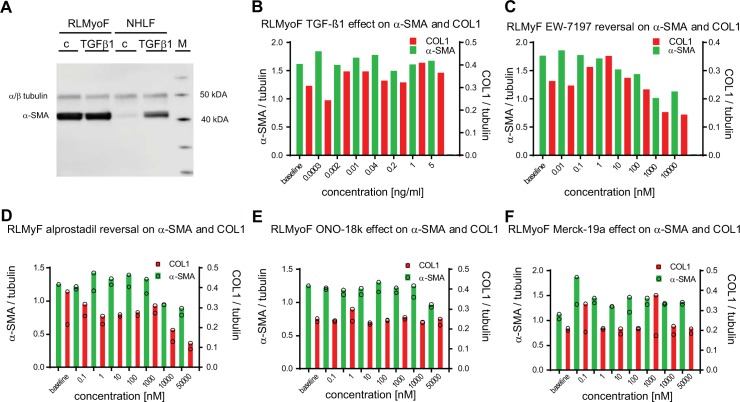
Fig 7. Effects on α–SMA and COL1 levels in primary myofibroblasts isolated from fibrotic lungs of bleomycin–instilled aged Wistar rats.
(A) Primary NHLF and myofibroblasts isolated from fibrotic rat lung middle lobes (RLMyoF) 28 days after bleomycin instillation were serum starved for 24 h and stimulated either with 5 ng / ml TGF–β1 (TGF–β) or with the appropriate vehicle control (c) for 48 h. α–SMA (42 kDa) and α / β–tubulin (50 kDa) were quantified by immunoblot analysis. The protein molecular weight marker (M) was run in parallel to estimate protein size. (B) RLMyoF were starved for 24 h, stimulated with a dilution series of TGF–β1 for 24 h, washed, cultured in the absence of TGF–β1 for further 72 h, and lysed to quantify α–SMA, COL1 and tubulin from single wells by MS / MS detection. (C–F) Non–stimulated RLMyoF were starved for 24 h and then exposed to increasing concentrations of compound for further 72 h. Cells were lysed and α–SMA (green bars) and COL1 (red bars) were quantified by MS / MS to assess the effect of the ALK5 inhibitor EW–7197 (C), alprostadil (D), and the EP2 and EP4 receptor selective agonists ONO–18k (E), and Merck–19a (F), respectively. All analytes were normalized to tubulin. 0.1% DMSO solvent was present in all wells. Number of sample (n = 1) in (B, C) and (n = 2) in (D–F).