Fig. 4. Projected future change in joint probability of simultaneous warm+dry conditions of varying severity.
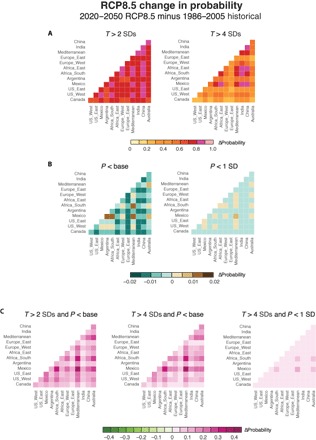
Colors show the probability (based on the Bayesian posterior mean) that both regions of a respective region pair experience severe conditions in the same year during the 2020–2050 period of the RCP8.5 simulations, expressed as the absolute difference from the probability in the CMIP5 historical simulations. (A) Joint probability for years in which the temperature anomaly is at least 2 SDs (left column) or 4 SDs (right column) warmer than the baseline mean. (B) Joint probability for years in which the precipitation anomaly is drier than the baseline mean (left column) or at least 1 SD drier than the baseline mean (right column). (C) Joint probability for years in which the temperature anomaly is at least 2 SDs warmer than the baseline mean and the precipitation anomaly is drier than the baseline mean (left column), the temperature anomaly is at least 4 SDs warmer than the baseline mean and the precipitation anomaly is drier than the baseline mean (center column), or the temperature anomaly is at least 4 SDs warmer than the baseline mean and the precipitation anomaly is at least 1 SD drier than the baseline mean (right column).
