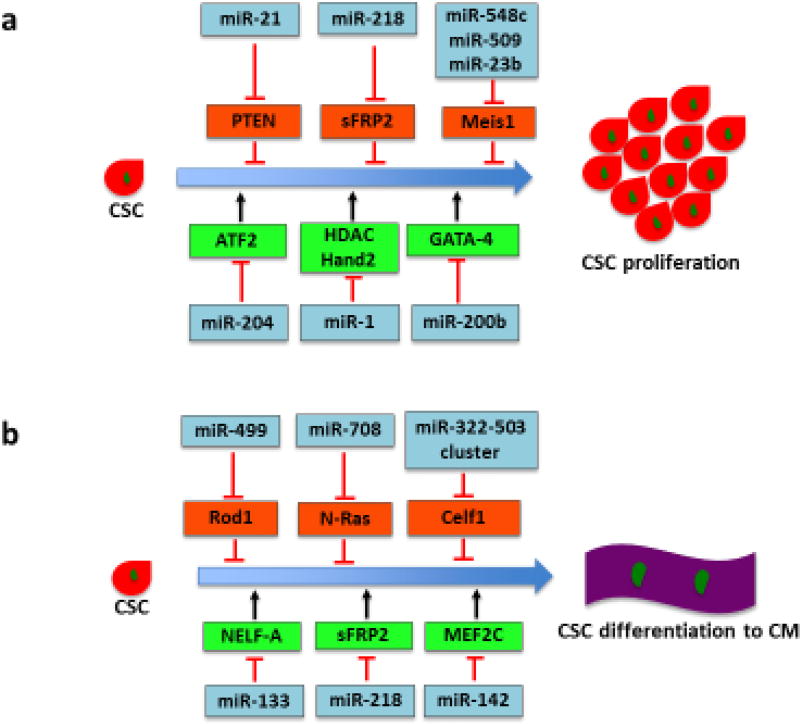
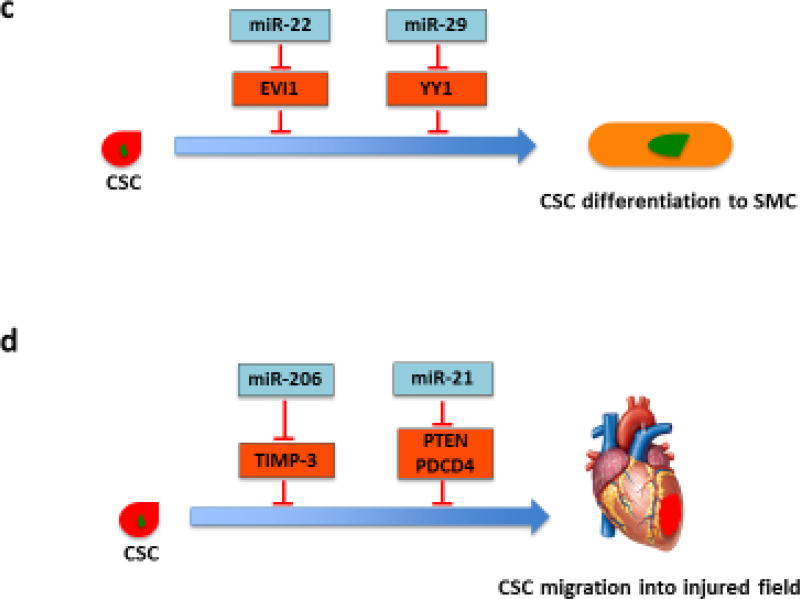
Figure 2.
Role of miRNAs in regulating CSC proliferation, differentiation and migration. (a) Various miRNAs regulate proliferation-related signaling pathways in CSCs. Several miRNAs, such as miR-21, miR-218, miR-548c, miR-509 and miR-23b, induce CSC proliferation by targeting negative regulators of cell proliferation, whereas miR-1, miR-200b and miR-204 inhibit CSC proliferation by modulating proliferation-related transcription factors. (b) Several miRNAs regulate CSC differentiation into CMs. miRNAs from the miR-322/-503 cluster (miR-499 as well as miR-708) promote CM commitment by suppressing the factors that inhibit cardiac differentiation. By contrast, miR-133 targets NELF-A, a nuclear factor promoting cardiogenesis. miR-218 and miR-142 inhibit CSC differentiation by modulating sFRP2, a negative regulator of proliferation, and cardiac transcription factor MEF2C, respectively. (c) miR-22 and miR-29 promote SMC commitment. Their targets, EVI1 and YY1, suppress the SMC marker gene expression and negatively regulate SMC transcription factors, respectively. (d) miR-206 and miR-21 have been shown to directly control migration of CSCs. Induction of CSC migration to injured heart could enhance cardiac regeneration. Abbreviations: ATF2, activating transcription factor 2; miRNAs, microRNAs; CSCs, cardiac stem cells; CMs, cardiomyocytes; SMC, smooth muscle cell; Celf1, CUG-binding protein Elav-like family member 1; EVI1, ecotropic virus integration site 1 protein homolog; GATA-4, GATA-binding protein 4; Hand 2, hand transcription factor 2; HDAC, histone deacetylase 4; MEF2C, myocyte enhancer factor 2C; NELF-A, negative elongation factor-A; PDCD4, programmed cell death 4; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; Rod1, regulator of differentiation 1; sFRP2, secreted frizzled-related protein 2; TIMP-3, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3; YY1, transcription factor Yin Yang 1.