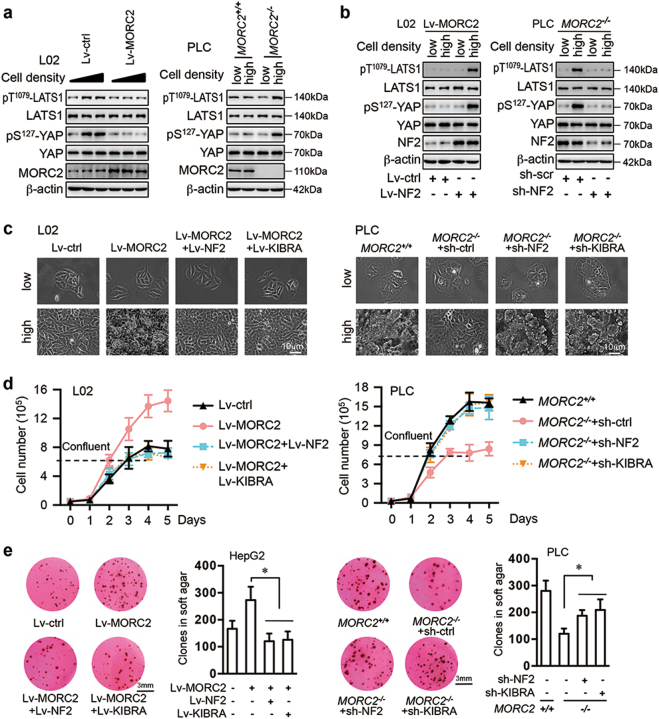
Fig. 5.
MORC2 modulates confluence-induced activation of Hippo signaling and growth arrest by suppressing NF2 and KIBRA expression. a MORC2 suppresses confluence-induced activation of Hippo signaling. Control (Lv-ctrl) and MORC2-expressing (Lv-MORC2) L02 cells, or MORC2+/+ and MORC2−/− PLC cells were seeded at different degree of confluence for 8 h. Cell lysates were collected for western blot analysis. b MORC2-expressing (Lv-MORC2) L02 cells were infected with control or NF2-encoding lentivirus. MORC2−/− PLC cells were infected with lentivirus delivering scramble shRNA or NF2-specific shRNA. The activity of Hippo signaling at low or high confluence was examined by western blot. c–e NF2 and KIBRA are critical downstream targets for MORC2 to override confluence-induced growth arrest. Control (Lv-ctrl) and MORC2-expressing (Lv-MORC2) cells were infected with empty vector or lentivirus encoding NF2 or KIBRA. Alternatively, MORC2+/+ and MORC2−/− cells were infected with lentivirus delivering scramble shRNA (sh-ctrl), NF2-, or KIBRA-specific shRNA. The morphologies of cells at low or high confluence were monitored by microscopy (c). The anchorage-dependent (d) and independent (e) growth capacities of these cells were examined and presented as mean ± SD. L02 cells and PLC cells were used for monitoring anchorage-dependent growth (c, d), while HepG2 and PLC cells were used for soft agar colony formation assay (e). Representative images from triplicate experiments are presented (a, b, c, e). *P < 0.05