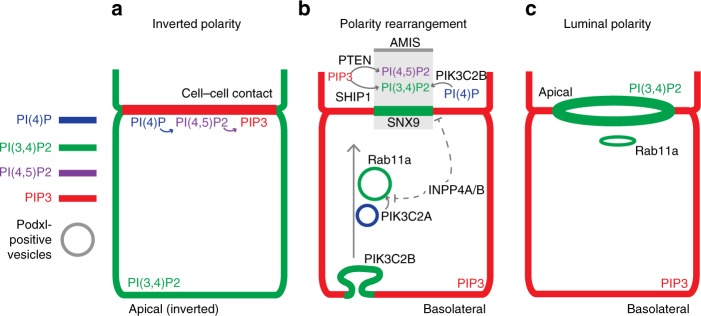
Fig. 10.
Model of PIP rearrangements during lumen formation. Shortly after plating into 3D, single MDCK cells undergo morphogenesis to form a cell doublet with initially inverted polarity a, whereby the apical surface marked by Podxl abuts the ECM. At this stage, a PI(4)P>PI(4,5)P2 > PIP3 cascade defines the cell–cell contact, while PI(3,4)P2 is inverted. b To reorient polarity, peripheral Podxl internalizes into vesicles which are initially PI(3)P and/or PI(4)P positive, before progressively enriching to become PI(3,4)P2/Rab11a-positive. These vesicles target to the apical membrane initiation site (AMIS). The PI(3,4)P2-promoting Class-II PI3Ks PIK3C2A/B promote, whereas the PI(3,4)P2-degrading phosphatases INPP4A/B inhibit, this process. Concomitantly, the AMIS is formed by two PIP phosphatases, PTEN and SHIP1, which focally convert PIP3 into, PI(4,5)P2 or PI(3,4)P2, respectively to form this zone for apical vesicle delivery. c Upon delivery of transcytosing Podxl, de novo lumen formation is completed, leaving cortical PI(4)P and PI(4,5)P2, basolateral PIP3, and apical and recycling endosome PI(3,4)P2