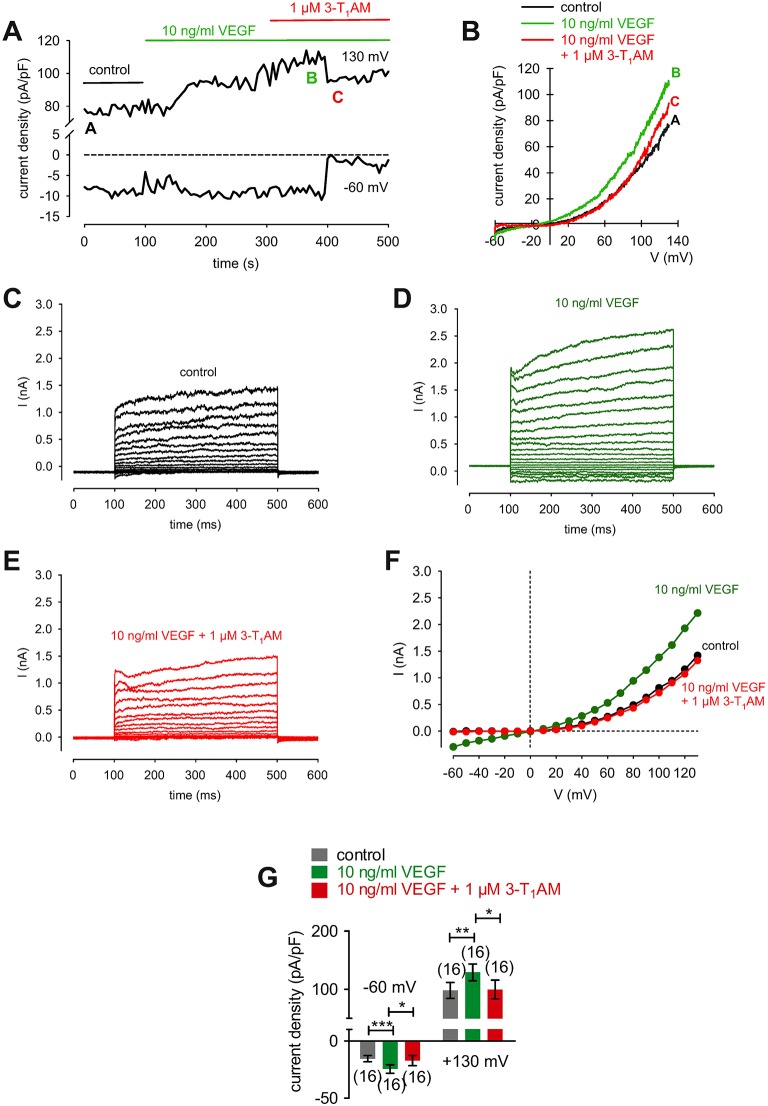
Figure 12.
3-T1AM suppresses VEGF-induced increases in whole-cell currents in HCK. (A) Time course recording showing the current increases induced by 10 ng/ml VEGF and current density levels after adding 3-T1AM (1 μM). There was a delayed increase and decrease of whole-cell currents, respectively. (B) Original traces of VEGF-induced current responses to voltage ramps. Current densities are shown before application (black labeled as A), during application of VEGF (green labeled as B), and after addition of 3T1AM (red labeled as C). Current densities as function of voltage were derived from the traces shown in (A). Notably, there was a decrease of VEGF-induced in- and outward currents in the presence of 3-T1AM. (C) Whole-cell currents under control conditions induced by depolarization from −60 to 130 mV in 10 mV steps (400 ms). (D) Increased whole-cell currents (green traces) in the presence of 10 ng/ml VEGF. (E) Decreased whole-cell currents (red traces) in the additional presence of 1 μM 3-T1AM. (F) Effect of VEGF and 3-T1AM summarized in a current/voltage plot [I-V plot, data obtained from (C–E)]. The black trace (filled circles) was obtained under control conditions. The green trace was obtained in the presence of 10 ng/ml VEGF and the lower red trace in the additional presence of 3-T1AM. An inhibitory effect could be observed. (G) Summary of the experiments with VEGF and 3-T1AM. The asterisks (*) indicate statistically significant differences of in- and outward currents with and without 3-T1AM (n = 16; p < 0.05 at the minimum; paired tested).