Figure 2.
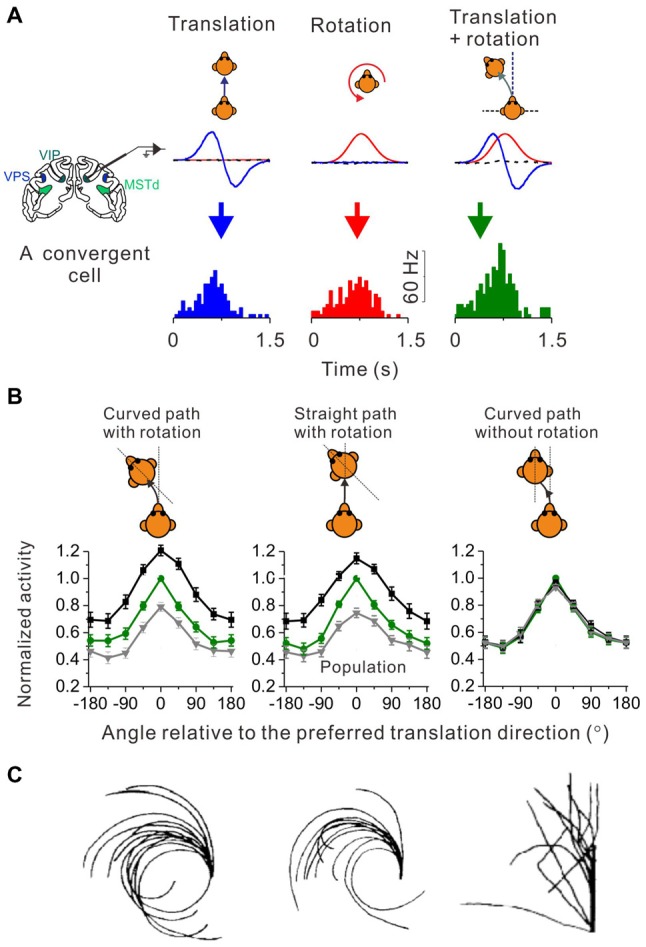
Identify cortical neurons responding to curvilinear self-motion. (A) Top panel: schematic illustration for three types of self-motion; middle panel: measured linear acceleration (Blue curve) and angular velocity (Red curve) for forward translation, CCW rotation and their corresponding curvilinear motion; Bottom panel: PSTH to forward translation, counter-clockwise (CCW) rotation and curvilinear motion with combined forward translation and CCW from an example convergent neuron in area VPS. (B) Firing rate pattern of convergent neurons from areas VPS, VIP and MSTd during curved-path-with-rotation, straight-path-with-rotation, and curved-path-without-rotation. Green curves: the translation only condition; black curves: curvilinear condition with preferred rotation; gray curves: curvilinear conditions with non-preferred rotation. Plots were made and modified with permission from Cheng and Gu (2016). (C) Trajectories drew by blinded-folded subjects after experiencing curved-path-with-rotation, straight-path-with-rotation and curved-path-without rotation delivered by a vehicle. Plots were made and modified with permission from Ivanenko et al. (1997).
