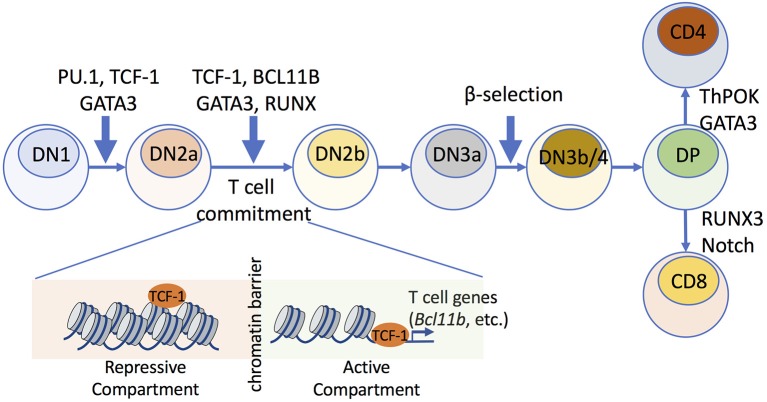
Figure 1.
Transcription factors that mediate chromatin accessibility during early thymic T cell development. Multiple TFs play roles in early stages of T cell maturation, which involve commitment of hematopoietic stem cells to T cell progenitors. The early DN stage consists of DN1, DN2a/b, DN3a/b, and DN4 cells. During T cell commitment, which occurs between the DN2a and DN2b stages, TCF-1 establishes chromatin accessibility and mediates compartment switch, where repressive compartments that harbor T cell-lineage-specific genes (e.g., Bcl11b) are switched to transcriptionally active compartments. TCF-1 upregulates the expression of BCL11B, which further remodels chromatin architecture and stabilizes the intra-TAD contacts within mature T cell subsets.