Figure 4.
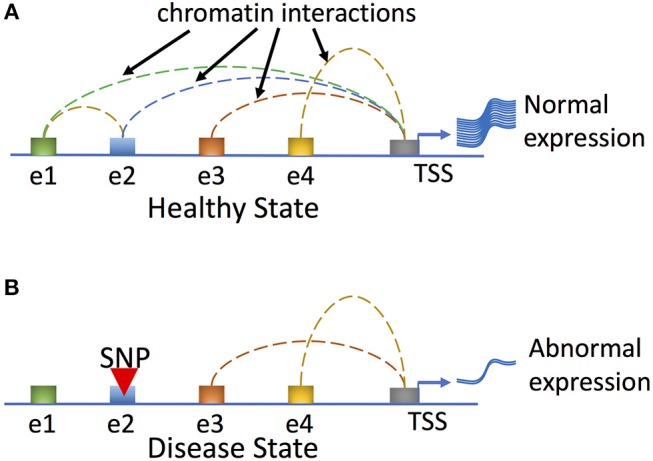
Genetic variation can affect human disease phenotypes by disrupting regulatory networks mediated by long-range chromatin interactions. In the healthy state (A), all regulatory enhancer elements (shown here for a hypothetical gene as elements e1–e4) are utilized and loop to the promoter to effect normal gene expression. In the disease state (B), a hypothetical genetic variant (SNP) residing at e2 disrupts enhancer-promoter and enhancer-enhancer interactions and results in abnormal gene expression and disease phenotypes.
