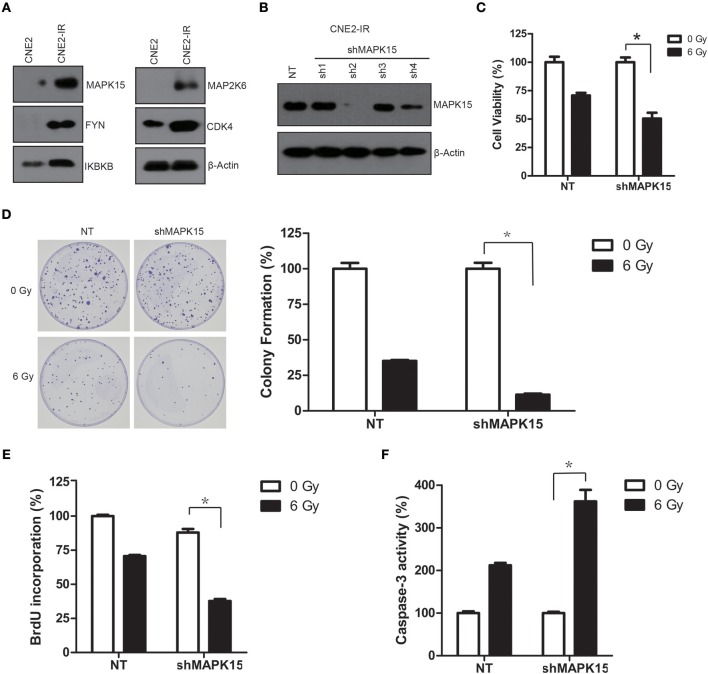
Figure 5.
High protein levels of MAPK15 regulate the radiosensitivity in CNE2-IR cells. (A) Western blotting validation on protein levels of five protein kinases (MAPK15, FYN, IKBKB, MAP2K6, and CDK4) in CNE2 and CNE2-IR cells. β-actin served as a loading control. (B) MAPK15 protein expression was significantly reduced in CNE2-IR cells transduced with shMAPK15 lentivirus (sh4). (C) Knockdown of MAPK15 increased radiosensitivity in CNE2-IR cells. The cell viability in NT or shMAPK15 without ionizing irradiation was regarded as 100%, respectively. shMAPK15 (6 Gy) vs. NT (6 Gy), n = 3 *P < 0.05. (D) Knockdown of MAPK15 attenuated colony formation after irradiation in CNE2-IR cells. The colony formation in NT or shMAPK15 without ionizing irradiation was regarded as 100%, respectively. shMAPK15 (6 Gy) vs. NT (6 Gy), n = 3, *P < 0.05. (E) Knockdown of MAPK15 impaired the proliferative potential of CNE2-IR cells exposed to irradiation. The BrdU incorporation in NT without ionizing irradiation was regarded as 100%. shMAPK15 (6 Gy) vs. NT (6 Gy), n = 4, *P < 0.05. (F) Knockdown of MAPK15 increased caspase-3 activity following irradiation in CNE2-IR cells. The caspase-3 activity in NT or shMAPK15 without ionizing irradiation was regarded as 100%, respectively. shMAPK15 (6 Gy) vs. NT (6 Gy), n = 4, *P < 0.05.