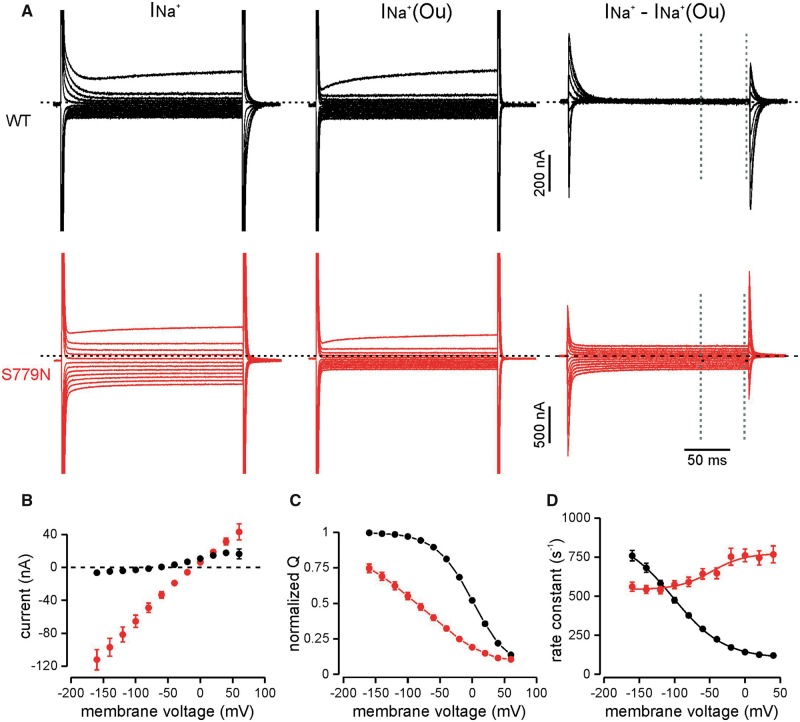
Figure 2.
Steady state and transient Na+ currents of WT and p.S779N pumps in the absence of extracellular K+. (A) Representative raw current traces in absence (left) and presence (middle) of 10 mM ouabain and the ouabain-sensitive currents (right) in wild-type (black) and p.S779N (red) pumps in response to voltage steps from −160 to +60 mV, in 20-mV increments. Steady state currents at each voltage were measured in the last 50 ms of the 200 ms stimulus, indicated by dotted lines. (B) Average ouabain-sensitive steady state leak currents. Slope conductance between −140 mV and 0 mV was 0.75 ± 0.08 nA/mV for the p.S779N pump (n = 27) while it was close to 0 for the wild-type pump (n = 29). (C) Charge-voltage relationships. Na+ charge transfer was determined from the integral of the first 50 ms of the current trace at −30 mV following the steps to test voltages. Individual QV curves were fit by a standard Boltzmann function and normalized to their respective fits. V1/2: p.S779N −95.4 ± 7.1 mV, n = 25; wild-type 2.6 ± 1.7 mV, n = 29; slope: p.S779N 66.8 ± 4.8 mV, wild-type 28.9 ± 0.7 mV, P < 10−5, unpaired t-test. (D) Rate constants of transient currents at the onset of the stimulus. Solid line represents a Boltzmann fit and yielded the overall forward/backward rate constants (p.S779N, 773.9 ± 27.7/542.6 ± 12.7 s−1, n = 22 wild-type 102.3 ± 3.6/882.2 ± 32.9 s−1, n = 26; P < 0.0001, unpaired t-test).