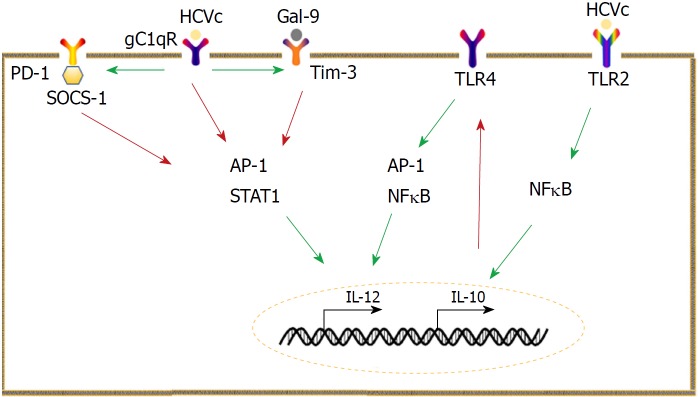
Figure 1.
Mechanisms underlying aberrant interleukin-10 and interleukin -12 expression. Monocytes are a main producer of interleukin-10 (IL-10) in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. HCV core protein (HCVc) can stimulate monocytes to produce IL-10, which selectively inhibits Toll-like receptor 4 signaling, leading to impairment of interleukin -12 (IL-12). Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)/ ligand of PD-1 (PD-L1) signaling and the galectin-9 (Gal-9)/ T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (Tim-3) pathways suppress IL-12 production by inhibiting activator protein 1 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 activation. The interaction between HCVc and receptor for the globular heads of C1q also inhibits IL-12 production but promotes PD-1/PD-L1 and Gal-9/Tim-3 pathways. The red arrow represents inhibition, whereas the green arrow indicates promotion. HCVc: HCV core protein; IL: Interleukin; TLR: Toll-like receptor; PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1: Ligand of PD-1; Gal-9: Galectin-9; TIM-3: T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3; AP-1: Activator protein 1; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; gC1qR: Receptor for the globular heads of C1q; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signaling; NFκB: Nuclear factor-κB.